The Purpose Of A Food Safety Management System Is To
Breaking News Today
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
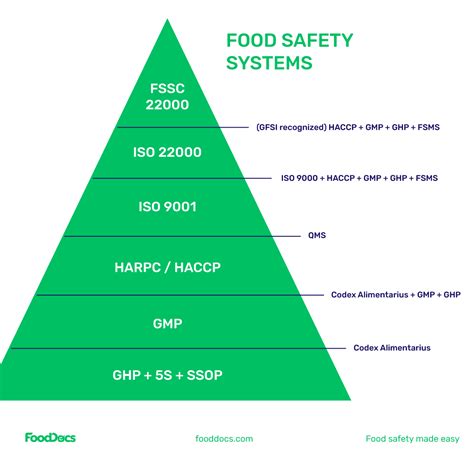
Table of Contents
The Purpose of a Food Safety Management System Is To… Protect Your Business and Your Customers
The purpose of a food safety management system (FSMS) is multifaceted, extending far beyond simply complying with regulations. It's a proactive approach to minimizing risks, ensuring consistent product quality, and ultimately, protecting public health. A robust FSMS safeguards your business reputation, prevents costly recalls, and fosters consumer trust. Let's delve into the core purposes of an effective FSMS.
Protecting Public Health: The Paramount Goal
At the heart of any FSMS lies the fundamental responsibility of protecting public health. Foodborne illnesses, caused by bacteria, viruses, parasites, or toxins, can range from mild discomfort to severe illness and even death. An effective FSMS minimizes the risks associated with these hazards by:
Identifying and Controlling Biological Hazards
- Bacterial Contamination: FSMS protocols cover procedures to control the growth of bacteria like Salmonella, E. coli, Listeria, and Campylobacter throughout the entire food production chain. This includes proper hygiene practices, temperature control, and effective sanitation.
- Viral Contamination: Viruses such as Norovirus and Hepatitis A can contaminate food through various pathways. An FSMS helps mitigate this risk through employee health policies, handwashing protocols, and preventing cross-contamination.
- Parasitic Contamination: Parasites like Toxoplasma gondii and Cyclospora cayetanensis can be present in certain foods. An FSMS includes measures to control these hazards, focusing on proper sourcing, handling, and cooking procedures.
Identifying and Controlling Chemical Hazards
- Pesticide Residues: FSMS incorporates strategies to monitor and control pesticide residues on produce. This may involve selecting suppliers with rigorous pesticide management programs and implementing testing procedures.
- Cleaning Chemicals: The system addresses the safe handling and storage of cleaning chemicals, preventing cross-contamination with food products. Proper labeling, designated storage areas, and training are essential components.
- Heavy Metals: An FSMS helps prevent contamination with heavy metals through careful sourcing of ingredients and adherence to processing guidelines.
Identifying and Controlling Physical Hazards
- Foreign Objects: Foreign bodies like glass, metal, or plastic can unintentionally contaminate food. An FSMS establishes procedures to minimize this risk through regular equipment inspections, employee training, and metal detection systems.
- Bone Fragments: In meat processing, measures are implemented to detect and remove bone fragments to prevent injuries and ensure product safety.
- Pest Control: An FSMS integrates pest control measures to prevent rodent and insect infestations, which can contaminate food and spread diseases.
Protecting Your Business: Financial and Reputational Safeguards
Beyond public health, a robust FSMS offers significant benefits to your business:
Preventing Costly Recalls
Food recalls can be incredibly expensive, involving significant financial losses from destroyed product, legal fees, and reputational damage. A well-implemented FSMS proactively identifies and mitigates potential hazards, reducing the likelihood of recalls and the associated costs. The financial impact of a recall can cripple a small business and severely impact even larger corporations. Proactive measures are far more cost-effective than reactive responses.
Maintaining Brand Reputation and Consumer Trust
Consumer trust is paramount in the food industry. A food safety incident can severely damage your brand reputation, leading to decreased sales and loss of market share. A demonstrably robust FSMS communicates to consumers your commitment to safety, reassuring them of the quality and integrity of your products. This builds consumer confidence and strengthens your brand's long-term viability.
Meeting Regulatory Requirements and Avoiding Penalties
Food safety regulations vary by region and jurisdiction, but all share the common goal of protecting consumers. Failing to meet these regulations can result in significant penalties, including fines, legal action, and even business closure. An FSMS ensures compliance with all applicable laws and regulations, avoiding costly penalties and maintaining a legal operating status. Knowing the regulations for your specific location and product is crucial.
Improving Operational Efficiency and Productivity
A well-designed FSMS streamlines processes, improving efficiency and minimizing waste. By standardizing procedures and enhancing traceability, you can reduce errors, optimize workflows, and improve overall productivity. This leads to cost savings and optimized resource allocation.
Enhancing Employee Morale and Safety
A food safety culture that emphasizes training, clear procedures, and employee empowerment boosts morale and reduces workplace accidents. Employees feel more confident and engaged when they understand their role in maintaining food safety.
Core Components of an Effective FSMS
Several key components contribute to a comprehensive and effective FSMS:
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP)
HACCP is a preventative approach to food safety that identifies potential hazards and establishes critical control points (CCPs) where hazards can be controlled. By monitoring these CCPs, you can ensure consistent product safety.
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and Good Agricultural Practices (GAP)
GMP and GAP cover fundamental hygiene and operational procedures across the food production process. These practices ensure a safe and clean environment for food handling, processing, and packaging.
Supplier Management
Selecting reliable suppliers who adhere to high food safety standards is crucial. An FSMS includes procedures for evaluating and selecting suppliers, monitoring their performance, and ensuring the safety of incoming ingredients.
Traceability and Recall Management
An effective FSMS incorporates systems for tracking products throughout the entire supply chain. This enables quick and efficient product tracing in case of a recall, minimizing the impact and ensuring customer safety.
Employee Training and Education
Regular employee training is essential to reinforce food safety protocols and ensure that all staff understand their responsibilities. Training should cover hygiene, hazard identification, proper procedures, and emergency response.
Documentation and Record Keeping
Meticulous documentation of all FSMS activities is essential for auditing, compliance, and continuous improvement. This includes records of training, inspections, CCP monitoring, and corrective actions.
Internal Audits and Management Review
Regular internal audits assess the effectiveness of the FSMS and identify areas for improvement. Management reviews ensure the system remains relevant, up-to-date, and aligns with evolving food safety standards.
Choosing the Right FSMS for Your Business
The specific requirements of an FSMS will vary depending on the type of food business, the scale of operations, and the types of products handled. Small businesses may need a simpler system, while larger companies may require a more comprehensive and sophisticated approach. Factors to consider include:
- Size and scope of your business: A small bakery will have different needs than a large-scale meat processing plant.
- Types of food products handled: Different food products pose different safety challenges.
- Regulatory requirements: Compliance with local and national regulations is paramount.
- Budgetary constraints: Choosing an FSMS that aligns with your budget is crucial.
- Technology and resources: Consider the technology and resources available to support your chosen FSMS.
Continuous Improvement: The Ongoing Process
An FSMS is not a static document; it's a dynamic system that requires ongoing review and improvement. Regular audits, employee feedback, and technological advancements all contribute to continuous improvement. This ongoing process ensures your FSMS remains effective and adapts to evolving safety standards and best practices. Embrace change and consistently strive to enhance your food safety protocols.
In conclusion, the purpose of a food safety management system is far-reaching, impacting public health, business operations, and brand reputation. By implementing and consistently upholding a robust FSMS, businesses demonstrate their commitment to safety, protect their customers, and safeguard their future. A comprehensive FSMS is not simply a regulatory requirement; it’s an investment in the success and sustainability of your business.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Ati Rn Comprehensive Predictor 2023 With Ngn Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
How Many Feet From A Helicopter Lifting Depositing Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Best Definition Of Marginal Revenue Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Superficial Temporal Artery Can Be Palpated Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
-
Rn Comprehensive Online Practice 2023 B With Ngn Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Purpose Of A Food Safety Management System Is To . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
