What Is The Best Definition Of Marginal Revenue Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
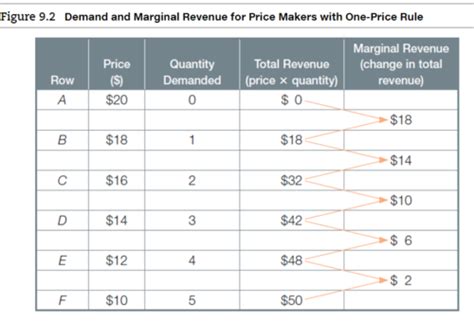
Table of Contents
Decoding Marginal Revenue: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding marginal revenue is crucial for any business aiming to maximize profits. While a quick search might lead you to simple definitions on platforms like Quizlet, a truly comprehensive understanding requires delving deeper into its nuances and implications. This article will provide a robust definition of marginal revenue, explore its calculation, explain its relationship with other economic concepts, and offer real-world applications to solidify your understanding.
What is Marginal Revenue? A Precise Definition
Marginal revenue (MR) is the additional revenue generated from selling one more unit of a good or service. It's not the total revenue earned, but the incremental revenue gained from that last sale. This concept is fundamental in microeconomics and plays a significant role in pricing strategies and production decisions.
Calculating Marginal Revenue: A Step-by-Step Approach
Calculating marginal revenue is straightforward. It involves comparing the total revenue generated at one quantity sold with the total revenue generated at a slightly higher quantity. The difference represents the marginal revenue.
-
Total Revenue (TR): This is the overall revenue earned from selling a specific quantity of goods or services. It's calculated by multiplying the price per unit (P) by the quantity sold (Q): TR = P x Q
-
Marginal Revenue (MR): This is the change in total revenue resulting from selling one more unit. Mathematically, it's expressed as: MR = ΔTR / ΔQ (where Δ represents "change in").
Example:
Let's say a company sells widgets. At a price of $10, they sell 100 widgets, generating a total revenue of $1,000 (100 x $10). If they increase sales to 101 widgets at the same price, their total revenue increases to $1,010. The marginal revenue from selling the 101st widget is $10 ($1,010 - $1,000 = $10).
Understanding Marginal Revenue in Different Market Structures
The behavior of marginal revenue varies significantly depending on the market structure a firm operates in.
1. Perfect Competition:
In a perfectly competitive market, firms are price takers – they cannot influence the market price. Therefore, the marginal revenue for each additional unit sold is equal to the market price. If the market price of a widget is $10, the marginal revenue from selling each widget is also $10. This is because selling one more unit doesn't affect the overall market price.
2. Monopoly:
Monopolies, on the other hand, have significant market power. To sell more units, they must lower their price. This means that the marginal revenue in a monopoly is always less than the price. As the monopolist sells more units, the price reduction affects the revenue generated from all previously sold units, resulting in a lower marginal revenue than the current selling price.
3. Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly:
These market structures fall between perfect competition and monopoly. Firms have some degree of market power, but it's less than a monopoly. The marginal revenue curve in these markets will slope downwards, but the decline will be less steep than in a monopoly.
Marginal Revenue and Profit Maximization:
A fundamental principle in economics is that firms aim to maximize profits. Marginal revenue plays a pivotal role in achieving this goal. Profit maximization occurs where marginal revenue equals marginal cost (MC).
- Marginal Cost (MC): This is the additional cost incurred from producing one more unit of a good or service.
When MR > MC, the firm can increase its profit by producing and selling more units. Conversely, if MR < MC, the firm should reduce its output to increase profitability. The point where MR = MC represents the optimal level of production for profit maximization.
Real-World Applications of Marginal Revenue:
Understanding marginal revenue is crucial in various real-world scenarios:
-
Pricing Decisions: Businesses use marginal revenue analysis to determine optimal pricing strategies. By understanding the relationship between price changes and the resulting changes in marginal revenue, companies can set prices that maximize their profits.
-
Production Decisions: Firms utilize marginal revenue and marginal cost analysis to determine the optimal quantity of goods or services to produce. Producing beyond the MR = MC point leads to diminishing returns and lower profits.
-
Market Entry and Exit: Analyzing marginal revenue and costs helps companies determine whether to enter a new market or exit an existing one. If the potential marginal revenue from entering a market doesn't cover the marginal cost, it's often not economically viable.
-
Investment Decisions: Marginal revenue analysis plays a role in making investment decisions. If the marginal revenue from a new investment project exceeds its marginal cost, it could be a worthwhile undertaking.
-
Competitive Analysis: Understanding the marginal revenue curves of competitors helps firms anticipate their pricing strategies and market actions, allowing for more effective strategic planning.
Marginal Revenue and Elasticity of Demand:
The relationship between marginal revenue and the elasticity of demand is significant. Elasticity refers to the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price.
-
Elastic Demand: When demand is elastic (a small price change leads to a large change in quantity demanded), marginal revenue is positive. Lowering the price increases revenue because the increase in quantity sold more than offsets the lower price.
-
Inelastic Demand: When demand is inelastic (a price change has a relatively small impact on quantity demanded), marginal revenue is negative. Lowering the price decreases revenue because the increase in quantity sold is not enough to offset the lower price.
-
Unitary Elastic Demand: When demand is unitary elastic, marginal revenue is zero. Any price change leaves total revenue unchanged.
Advanced Concepts Related to Marginal Revenue
Beyond the basics, several advanced concepts build upon the understanding of marginal revenue:
-
Marginal Revenue Product (MRP): This concept extends the idea of marginal revenue to the context of labor. MRP measures the additional revenue generated by hiring one more unit of labor.
-
Marginal Revenue Curve: Graphically representing the relationship between marginal revenue and quantity sold. This curve helps visualize the profit-maximizing output level.
-
Imperfect Competition and Marginal Revenue: In markets with imperfect competition (monopoly, oligopoly, monopolistic competition), the marginal revenue curve lies below the demand curve, reflecting the impact of price changes on total revenue.
-
Dynamic Pricing: Advanced pricing strategies, such as dynamic pricing (adjusting prices in real-time based on demand), rely heavily on real-time analysis of marginal revenue and cost.
Conclusion: Mastering the Concept of Marginal Revenue
Understanding marginal revenue is not just about memorizing a definition from Quizlet. It's about grasping a fundamental economic concept that underpins numerous business decisions. By understanding its calculation, its behavior in different market structures, and its relationship with other key concepts like marginal cost and elasticity of demand, you gain a powerful tool for analyzing business performance, formulating effective pricing strategies, and ultimately maximizing profitability. The deeper your understanding, the more effectively you can apply these principles in real-world scenarios, whether you're a student of economics or a seasoned business professional.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
True Or False Professional And Technical Communication Is Research Oriented
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Best Describes The Terrorist Planning Cycle
Mar 18, 2025
-
Cdl Combination Test Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
Life Insurance Exam Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Direct Carry Is Used To Transfer A Patient
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Best Definition Of Marginal Revenue Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
