The Responsibilities Of The Operations Manager Include
Breaking News Today
Mar 29, 2025 · 6 min read
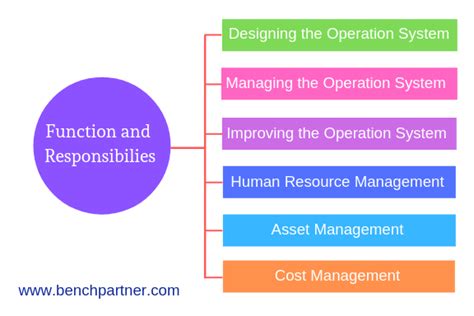
Table of Contents
The Extensive Responsibilities of an Operations Manager: A Deep Dive
The operations manager plays a pivotal role in the success of any organization, regardless of size or industry. They are the linchpin connecting strategy and execution, ensuring smooth daily operations and driving continuous improvement. This article delves deep into the multifaceted responsibilities of an operations manager, exploring the key areas they oversee and the skills required to excel in this demanding yet rewarding role.
Core Responsibilities: The Foundation of Operational Excellence
At the heart of an operations manager's role lies the responsibility of overseeing the daily operations of the business. This encompasses a broad spectrum of activities, demanding a versatile skillset and a proactive approach to problem-solving.
1. Strategic Planning and Goal Setting:
- Developing Operational Strategies: Operations managers are not simply reactive; they are proactive strategic thinkers. They work closely with senior management to develop comprehensive operational strategies aligned with the overall business goals. This includes setting key performance indicators (KPIs) and establishing measurable targets for efficiency, productivity, and quality.
- Resource Allocation: Effective resource allocation is crucial for optimal performance. This includes managing budgets, allocating personnel, and optimizing the use of equipment and technology. Operations managers must make informed decisions about resource distribution to maximize output and minimize waste.
- Forecasting and Capacity Planning: Predicting future demands and adjusting operational capacity accordingly is a vital responsibility. This involves analyzing market trends, sales projections, and production capacity to ensure the organization can meet current and future demands efficiently.
2. Process Improvement and Optimization:
- Identifying Bottlenecks and Inefficiencies: A core function is identifying areas where operational processes can be improved. This requires a keen eye for detail, a systematic approach to analysis, and the ability to identify bottlenecks that hinder efficiency.
- Implementing Lean Principles and Six Sigma Methodologies: Many operations managers leverage lean principles and Six Sigma methodologies to streamline processes, reduce waste, and improve quality. This requires understanding and implementing these methodologies to optimize workflows and minimize errors.
- Automation and Technology Integration: Embracing technological advancements is crucial for operational efficiency. Operations managers explore and implement automation tools and technologies to streamline processes, improve data analysis, and enhance overall productivity.
3. Team Management and Leadership:
- Supervising and Motivating Teams: Operations managers are responsible for leading and managing teams of employees. This includes providing guidance, setting clear expectations, fostering a positive work environment, and motivating team members to achieve shared goals.
- Performance Management and Development: Regular performance reviews, constructive feedback, and opportunities for professional development are essential for team growth. Operations managers play a key role in identifying training needs, mentoring employees, and fostering a culture of continuous learning.
- Recruitment and Selection: In many organizations, operations managers are involved in the recruitment and selection process for their teams. This includes defining job requirements, conducting interviews, and making hiring decisions based on skills and experience.
4. Quality Control and Assurance:
- Establishing Quality Standards: Setting and maintaining high quality standards is paramount. This involves defining clear quality metrics, establishing robust quality control processes, and ensuring adherence to industry regulations and best practices.
- Implementing Quality Control Measures: Implementing and monitoring quality control procedures is crucial for ensuring consistent product or service quality. This includes conducting regular inspections, implementing feedback mechanisms, and proactively addressing quality issues.
- Continuous Improvement Initiatives: Quality is not a static achievement; it's an ongoing journey. Operations managers champion continuous improvement initiatives, analyzing quality data, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing corrective actions.
5. Supply Chain Management:
- Vendor Relationship Management: Building and maintaining strong relationships with vendors and suppliers is vital for a smooth and reliable supply chain. This includes negotiating contracts, managing inventory, and ensuring timely delivery of materials.
- Inventory Management: Efficient inventory management is crucial for minimizing storage costs, preventing stockouts, and ensuring optimal production flow. Operations managers develop and implement strategies for inventory control, forecasting demand, and managing warehouse operations.
- Logistics and Distribution: Operations managers are often involved in managing logistics and distribution networks, ensuring efficient transportation of goods and services to customers. This includes overseeing shipping, delivery, and handling procedures.
Expanding Responsibilities: Adapting to the Modern Landscape
The responsibilities of an operations manager are constantly evolving, influenced by technological advancements, globalization, and changing market dynamics. Several key areas reflect this expansion:
6. Data Analytics and Reporting:
- Performance Monitoring and Analysis: Operations managers increasingly rely on data analytics to monitor performance, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions. This includes analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs), identifying areas for improvement, and using data to inform strategic planning.
- Business Intelligence and Reporting: Providing regular reports and insights into operational performance to senior management is critical. This involves creating clear and concise reports that effectively communicate key findings and support strategic decision-making.
- Predictive Analytics and Forecasting: Utilizing predictive analytics to anticipate future trends and optimize operational strategies is becoming increasingly important. This allows for proactive adjustments to resource allocation, capacity planning, and supply chain management.
7. Risk Management and Compliance:
- Identifying and Mitigating Risks: Operations managers are responsible for identifying and mitigating potential risks to the organization's operations. This includes assessing potential threats, developing contingency plans, and implementing preventative measures.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to relevant regulations and industry standards is crucial. Operations managers ensure compliance with health and safety regulations, environmental standards, and other legal requirements.
- Crisis Management: Developing and executing crisis management plans is vital for effectively handling unexpected events and minimizing their impact on the organization.
8. Sustainability and Corporate Social Responsibility:
- Implementing Sustainable Practices: Increasingly, organizations are prioritizing sustainability initiatives. Operations managers play a role in implementing environmentally friendly practices, reducing waste, and promoting energy efficiency.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Many operations managers are involved in integrating CSR initiatives into the organization's operations. This might include supporting community programs, promoting ethical sourcing, and fostering a culture of social responsibility.
9. Innovation and Technology Adoption:
- Exploring New Technologies: Staying abreast of technological advancements and exploring new technologies to improve operational efficiency is crucial. This includes researching new software, automation tools, and other technologies that can enhance productivity and streamline processes.
- Digital Transformation: Leading the organization's digital transformation efforts is increasingly becoming a part of the operations manager's role. This involves identifying opportunities to leverage technology to improve efficiency, enhance customer experience, and gain a competitive advantage.
Essential Skills for Successful Operations Management
To excel in this multifaceted role, operations managers need a diverse skillset that encompasses both technical expertise and leadership qualities.
- Analytical Skills: Strong analytical skills are critical for analyzing data, identifying trends, and making informed decisions.
- Problem-Solving Skills: The ability to effectively identify and solve problems is essential for maintaining smooth operations and addressing challenges proactively.
- Communication Skills: Excellent communication skills are crucial for effectively communicating with team members, senior management, and external stakeholders.
- Leadership Skills: Motivating and inspiring teams, delegating effectively, and fostering a collaborative work environment are essential leadership qualities.
- Project Management Skills: Managing multiple projects simultaneously, prioritizing tasks, and meeting deadlines effectively are vital skills for operations managers.
- Technical Skills: Understanding of relevant software, technologies, and industry best practices is essential for optimizing operational processes.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Evolution of the Operations Manager's Role
The responsibilities of an operations manager are extensive and constantly evolving. Their role is no longer just about overseeing day-to-day operations; it's about strategic planning, process optimization, team leadership, and adapting to a rapidly changing business landscape. The successful operations manager is a blend of strategic thinker, problem-solver, leader, and innovator, constantly striving for efficiency, quality, and continuous improvement. The impact they have on an organization's overall success cannot be overstated.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Functions Of The Liver Include Quizlet Emt
Mar 31, 2025
-
An Application Programming Interface Api Is Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
Dental Disease Dates Back To The Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
Basic Functions Of The Liver Include Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
A Resident On Transmission Based Precautions Must Be Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Responsibilities Of The Operations Manager Include . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
