The Two Types Of Vehicle Braking Systems Are
Breaking News Today
Mar 22, 2025 · 7 min read
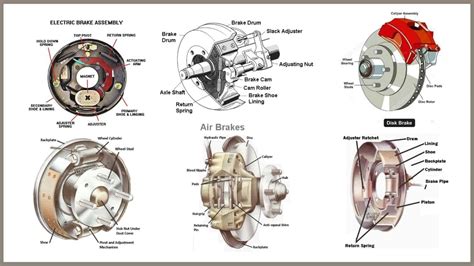
Table of Contents
The Two Main Types of Vehicle Braking Systems: A Deep Dive
Choosing the right braking system is crucial for the safety and performance of any vehicle. From the simplest bicycle to the most advanced Formula 1 car, effective braking is paramount. While braking systems have evolved significantly over the years, they all fall under two primary categories: drum brakes and disc brakes. This comprehensive guide will explore the intricacies of each, comparing their strengths and weaknesses, and clarifying which system might be best suited for various applications.
Drum Brakes: A Look Back at a Reliable System
Drum brakes, a technology that has been around for over a century, are a relatively simple and robust braking system. They operate using friction between brake shoes and a rotating drum, typically integrated into the wheel hub. This friction converts kinetic energy (motion) into heat, slowing and ultimately stopping the vehicle.
How Drum Brakes Work: The Mechanics
-
Brake Pedal Activation: When the brake pedal is pressed, hydraulic pressure is generated in the master cylinder.
-
Hydraulic Pressure Transmission: This pressure is transmitted through brake lines to the wheel cylinders located within the brake drum assembly.
-
Wheel Cylinder Expansion: The pressure causes the wheel cylinders to expand, pushing outward on the brake shoes.
-
Friction Engagement: The brake shoes, which are lined with friction material, press against the inner surface of the rotating brake drum.
-
Friction-Induced Deceleration: This friction creates resistance, slowing the rotation of the wheel and ultimately the vehicle.
-
Heat Dissipation: The friction process generates significant heat, which must be dissipated effectively to prevent brake fade (a reduction in braking performance due to overheating).
Advantages of Drum Brakes
- Cost-Effective: Drum brakes are generally less expensive to manufacture and maintain compared to disc brakes. This makes them a popular choice for budget-conscious vehicles.
- Self-Adjusting Mechanisms: Many drum brake systems incorporate self-adjusting mechanisms that automatically compensate for wear on the brake shoes, reducing the need for frequent manual adjustments.
- Relatively Simple Design: The simpler design translates to fewer potential points of failure and easier repairs in many cases.
- Effective in Wet Conditions: The enclosed nature of the drum brake system can offer better performance in wet conditions, as water is less likely to interfere with the braking action compared to exposed disc brakes. However, this advantage is increasingly being mitigated by advancements in disc brake technology.
- Good Parking Brake Integration: Drum brakes are often integrated with the parking brake system, providing a reliable and effective means of securing the vehicle when parked.
Disadvantages of Drum Brakes
- Limited Heat Dissipation: The enclosed nature of the drum, while beneficial in wet conditions, hinders effective heat dissipation. This can lead to brake fade under heavy braking, especially during prolonged or high-performance driving.
- Less Precise Control: Drum brakes generally offer less precise control and responsiveness compared to disc brakes, particularly in emergency situations. The force applied to the brake pedal may not translate directly and linearly to braking force.
- Susceptible to Wear and Tear: The brake shoes are subject to wear and require periodic replacement. Furthermore, the drum itself can become scored or damaged over time, requiring replacement or machining.
- Less Effective in High-Performance Applications: Due to the limitations in heat dissipation and control, drum brakes are not well-suited for high-performance vehicles demanding consistent and strong braking under demanding conditions.
- More Difficult Inspection: Inspecting the condition of the drum brake system is more challenging than with disc brakes. It requires disassembly to assess the wear of the brake shoes and the drum's condition.
Disc Brakes: The Modern Standard for Superior Performance
Disc brakes have become increasingly prevalent in modern vehicles due to their superior performance characteristics. Unlike drum brakes, they utilize a caliper clamping a rotating disc to generate braking force. This design offers several advantages, making them the preferred choice for many applications.
How Disc Brakes Work: A Detailed Look
-
Brake Pedal Activation: Similar to drum brakes, pressing the brake pedal creates hydraulic pressure in the master cylinder.
-
Hydraulic Pressure Transmission: This pressure is transmitted through brake lines to the brake calipers, positioned on either side of the brake disc.
-
Caliper Piston Movement: The pressure forces the caliper pistons outward, pressing the brake pads against the rotating disc.
-
Friction Engagement: The friction between the brake pads (lined with friction material) and the disc creates resistance, slowing down the wheel.
-
Heat Dissipation: Disc brakes are significantly better at dissipating heat. The disc's large surface area and open design allow for efficient heat transfer to the surrounding air.
-
Deceleration: The resulting friction slows the rotation of the wheel and, consequently, the vehicle.
Advantages of Disc Brakes
- Superior Stopping Power: Disc brakes offer significantly more stopping power compared to drum brakes, especially under high-performance conditions. This is due to a larger contact area and better heat dissipation.
- Improved Control and Responsiveness: Disc brakes provide superior control and responsiveness, allowing for more precise braking modulation, particularly crucial in emergency situations. The driver experiences a more linear and predictable braking response.
- Excellent Heat Dissipation: The open design and large surface area of the disc allow for efficient heat dissipation, preventing brake fade and maintaining consistent braking performance under heavy use.
- Easier Inspection and Maintenance: Inspecting and maintaining disc brakes is relatively easy. The components are readily accessible, allowing for straightforward checks of pad wear and disc condition.
- Better Fade Resistance: Disc brakes are far less susceptible to brake fade than drum brakes. Their superior heat dissipation capabilities allow them to maintain braking performance even under extreme conditions.
Disadvantages of Disc Brakes
- Higher Cost: Disc brakes are typically more expensive to manufacture and maintain compared to drum brakes. The replacement cost of pads and rotors can be higher than for brake shoes and drums.
- Potential for Rust: Disc brakes, being exposed to the elements, are more susceptible to rust, especially in areas with high humidity. This can lead to increased noise or reduced braking effectiveness.
- More Complex Design: Disc brake systems have a more complex design than drum brakes, potentially leading to more points of potential failure, although modern designs minimize these risks.
- Less Effective in Extremely Muddy or Deep Water Conditions: While significantly improved compared to older designs, disc brakes can still be affected by severe mud or water buildup, potentially leading to temporary loss of braking performance. However, this is often a minor issue compared to their overall advantages.
- Parking Brake Integration Complexity: Integrating a parking brake system into disc brakes can be more complex, and often necessitates a separate parking brake mechanism such as a cable-actuated caliper.
Disc vs. Drum: The Verdict
The choice between disc and drum brakes depends largely on the application and priorities. While drum brakes offer a cost-effective and relatively simple solution, particularly for lighter vehicles and less demanding situations, disc brakes represent the superior technology for most modern vehicles. Their enhanced stopping power, improved control, and superior fade resistance make them the clear winner for performance-oriented applications, and increasingly the standard for everyday vehicles.
Modern advancements in both drum and disc brake technology continue to improve their performance and safety features. Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS), Electronic Brake-force Distribution (EBD), and Brake Assist (BA) are examples of safety features that work with both systems to maximize braking efficacy and driver safety.
The Future of Vehicle Braking Systems: Beyond Traditional Designs
While drum and disc brakes remain the dominant technologies, the future holds exciting possibilities for further advancements in braking systems. Here are a few areas of focus:
- Regenerative Braking: This system harnesses the kinetic energy of the vehicle during braking, converting it into electricity that can recharge the battery in electric and hybrid vehicles. This enhances efficiency and extends the vehicle's range.
- Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS): ADAS features, including automatic emergency braking (AEB) and adaptive cruise control (ACC), utilize sophisticated sensors and algorithms to automatically apply the brakes in certain situations, preventing or mitigating collisions.
- Brake-by-Wire Systems: These systems replace traditional hydraulic or mechanical linkages with electronic control systems, providing enhanced responsiveness, control, and the potential for more sophisticated braking strategies.
- Material Science Advancements: Ongoing research focuses on developing new materials for brake pads and discs, improving friction characteristics, wear resistance, and heat dissipation.
In conclusion, while drum brakes offer a cost-effective solution for certain applications, disc brakes stand as the more versatile and efficient choice for modern vehicles, particularly given their superior stopping power, control, and fade resistance. The continued evolution of braking technologies promises even greater safety and performance in the years to come, further enhancing the overall driving experience and contributing to safer roads.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Type Of Mutation Causes Sickle Cell Anemia Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
Delegates To The National Conventions Are Chosen Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
Anatomy And Physiology 2 Final Exam Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
Which Sexually Transmitted Infection Is Caused By Human Papillomavirus Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
-
The Person Centered Implementation Plan Should Include Quizlet
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Two Types Of Vehicle Braking Systems Are . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
