What Is The Cause Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
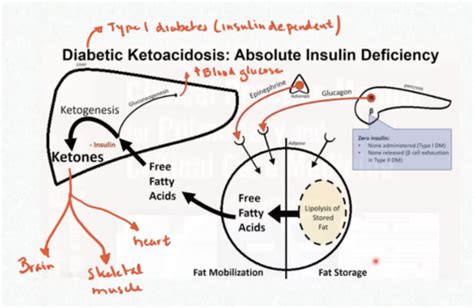
Table of Contents
What is the Cause of Diabetic Ketoacidosis? A Comprehensive Guide
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body doesn't have enough insulin. This lack of insulin leads to a buildup of ketones in the blood, which can be life-threatening. Understanding the underlying causes of DKA is crucial for prevention and effective management. This comprehensive guide explores the multifaceted reasons behind DKA development, delving into both the physiological mechanisms and contributing factors.
What is Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)?
Before diving into the causes, let's briefly revisit the definition of DKA. DKA is a metabolic state characterized by:
- Hyperglycemia: Abnormally high blood glucose levels.
- Ketone Production: The body breaks down fat for energy, producing ketones as a byproduct. These ketones accumulate in the blood, making it acidic.
- Acidosis: The increased acidity of the blood disrupts various bodily functions.
- Dehydration: Excessive urination due to hyperglycemia leads to fluid loss and dehydration.
These symptoms often manifest as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, shortness of breath, and fruity-smelling breath (due to acetone, a type of ketone). Without prompt treatment, DKA can lead to coma and death.
The Primary Cause: Insulin Deficiency
At the heart of DKA lies insulin deficiency. Insulin is a hormone crucial for regulating blood glucose levels. It allows glucose to enter cells from the bloodstream, providing energy. When insulin is insufficient, glucose cannot enter cells effectively, leading to:
- Elevated Blood Glucose: Glucose accumulates in the blood, causing hyperglycemia.
- Fat Breakdown: The body, deprived of glucose as fuel, switches to burning fat for energy. This process generates ketones.
- Ketoacidosis: The accumulation of ketones makes the blood acidic, resulting in ketoacidosis.
Types of Insulin Deficiency:
Insulin deficiency contributing to DKA can manifest in two primary ways:
-
Absolute Insulin Deficiency: This occurs when the pancreas doesn't produce enough insulin, typically seen in type 1 diabetes. The body's immune system attacks the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, severely limiting or eliminating insulin production.
-
Relative Insulin Deficiency: This occurs when the body produces some insulin, but it's insufficient to meet the demands of the body, particularly during periods of stress or illness. This is commonly seen in type 2 diabetes, often triggered by infections, illness, or inadequate insulin therapy.
Contributing Factors to DKA:
While insulin deficiency is the primary driver, several factors can precipitate or worsen DKA:
1. Infection: Infections, whether minor or severe, are a major trigger for DKA. Infections increase the body's demand for insulin, while simultaneously impairing insulin production or action. Examples include pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and gastroenteritis. The body's inflammatory response during infection further exacerbates insulin resistance.
2. Illness or Stress: Any significant illness or stressor places the body under considerable metabolic strain. This increased demand for energy often overwhelms the body's ability to regulate glucose, especially in individuals with inadequate insulin levels. Examples include heart attack, stroke, and pancreatitis. The body releases stress hormones like cortisol and glucagon, which raise blood sugar levels and further contribute to DKA.
3. Poor Diabetes Management: Inadequate management of diabetes, including inconsistent insulin administration, missed doses, or improper insulin adjustments, significantly increases the risk of DKA. This is particularly relevant in individuals with type 1 diabetes who rely solely on external insulin for survival. In type 2 diabetes, inadequate control of blood sugar levels through lifestyle changes or medication can also precipitate DKA.
4. Medication: Certain medications can interfere with insulin function or increase blood glucose levels, contributing to the development of DKA. Some examples include corticosteroids (like prednisone), diuretics, and some antipsychotic medications. These medications can induce insulin resistance or promote glucose production.
5. New-onset Type 1 Diabetes: In individuals newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes, the complete absence of insulin production can rapidly lead to DKA. Without prompt diagnosis and treatment, this can be a life-threatening emergency.
6. Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol intake can interfere with glucose metabolism and gluconeogenesis, indirectly contributing to increased blood glucose levels and potentially precipitating DKA. Alcohol can also deplete the body's stores of glycogen, further accelerating the process.
7. Pregnancy: Pregnancy can increase insulin resistance and, in individuals with pre-existing diabetes, increase the risk of DKA, particularly during the first trimester. The hormonal changes during pregnancy significantly impact insulin requirements.
8. Other Underlying Conditions: Certain underlying medical conditions, such as pancreatitis or certain gastrointestinal disorders, can increase the susceptibility to DKA. These conditions may directly or indirectly impact insulin production or action.
Symptoms of Diabetic Ketoacidosis:
Recognizing the symptoms of DKA is critical for timely intervention. These symptoms typically develop over a period of hours or days and can include:
- Excessive thirst and frequent urination: The body tries to eliminate excess glucose through urine, leading to dehydration.
- High blood glucose levels: Confirmed through blood testing.
- Dry mouth and skin: Due to dehydration.
- Fruity-smelling breath: The characteristic smell of acetone.
- Nausea and vomiting: Common symptoms of DKA.
- Abdominal pain: Can be a significant symptom.
- Weakness and fatigue: Due to dehydration and energy imbalance.
- Shortness of breath: Caused by the metabolic acidosis.
- Confusion or disorientation: As acidosis progresses.
- Loss of consciousness: In severe cases.
Diagnosis and Treatment of DKA:
Diagnosis involves blood tests to measure blood glucose, ketones, and blood pH (acidity). Treatment is aimed at restoring fluid balance, correcting acidosis, and managing blood glucose levels. This usually involves intravenous fluid administration, insulin therapy, and electrolyte replacement.
Prevention of DKA:
Preventing DKA involves diligent management of diabetes:
- Regular blood glucose monitoring: This allows for early detection of rising glucose levels.
- Consistent insulin therapy: For individuals with type 1 diabetes, adhering to the prescribed insulin regimen is crucial.
- Healthy lifestyle choices: Maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, and managing stress are vital.
- Prompt treatment of infections: Addressing infections swiftly helps prevent DKA.
- Regular follow-up with healthcare providers: Consistent monitoring and adjustments to the diabetes management plan help prevent complications.
In Conclusion:
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious condition arising primarily from insulin deficiency. While absolute insulin deficiency in type 1 diabetes is a key factor, relative deficiency exacerbated by various factors, including infections, illness, poor diabetes management, and medications, significantly contributes to DKA. Understanding these causes, recognizing the symptoms, and implementing effective preventative measures are crucial for managing diabetes and preventing this life-threatening complication. This comprehensive overview highlights the complex interplay of factors contributing to DKA, emphasizing the importance of proactive diabetes management and prompt medical attention should symptoms arise. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional are paramount in preventing and managing this serious condition.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Benefits Provided By A Medicare Supplement Policy Must Not
Mar 26, 2025
-
Wall Street Prep Excel Crash Course Exam Answers
Mar 26, 2025
-
Which Level Of Anxiety Enhances The Clients Learning Abilities
Mar 26, 2025
-
A Certifying Officers Certification Attests To The Legality
Mar 26, 2025
-
In Albert Banduras Social Cognitive Theory Behavior Refers To
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Cause Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
