What Is The Main Goal Of Prenatal Screening Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
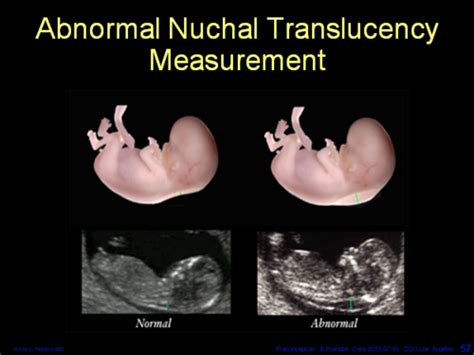
Table of Contents
What is the Main Goal of Prenatal Screening? A Comprehensive Guide
Prenatal screening, a cornerstone of modern obstetrics, plays a crucial role in ensuring a healthy pregnancy and the well-being of both mother and child. But what exactly is its main goal? It's not simply about identifying problems; it's a far more nuanced process aimed at empowering expectant parents with information to make informed decisions about their pregnancy journey. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the core objectives of prenatal screening, exploring its various components, benefits, limitations, and the ethical considerations involved.
The Primary Goal: Informed Decision-Making
The overarching goal of prenatal screening is to provide expectant parents with critical information to make informed decisions about their pregnancy. This involves assessing the risk of various fetal abnormalities and genetic conditions. This information allows parents to:
- Plan for potential challenges: Early identification of potential problems gives parents time to prepare emotionally, financially, and logistically for the birth of a child with special needs.
- Seek specialized care: Prenatal screening often leads to referrals to specialists like geneticists or maternal-fetal medicine experts, ensuring the best possible care for both the mother and the baby.
- Choose appropriate management strategies: Based on the screening results, parents can choose from various management strategies, including further diagnostic testing, fetal therapies, or preparation for specific medical interventions after birth.
- Reduce anxiety and uncertainty: While screening can reveal potential problems, it can also alleviate anxiety by ruling out certain conditions, providing peace of mind for many expecting parents.
Types of Prenatal Screening Tests
Prenatal screening encompasses a wide array of tests, each with its own specific goals and limitations. Some of the most common types include:
1. First-Trimester Screening:
This screening, typically performed between 11 and 13 weeks of gestation, combines two tests:
- Ultrasound: Measures the nuchal translucency (NT), the fluid accumulation at the back of the fetal neck. Increased NT is associated with an increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities like Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome).
- Blood Tests: Measure levels of pregnancy-associated plasma protein A (PAPP-A) and free beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG). Abnormal levels of these markers can also indicate an increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
Main Goal: To detect early signs of chromosomal abnormalities and other fetal abnormalities.
2. Second-Trimester Screening:
This screening, usually performed between 15 and 20 weeks of gestation, typically involves:
- Blood Tests: Measures levels of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), unconjugated estriol (uE3), human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), and inhibin A. Abnormal levels can indicate neural tube defects (like spina bifida), chromosomal abnormalities, or other fetal problems.
- Ultrasound: Provides a detailed anatomical survey of the fetus to assess for structural abnormalities.
Main Goal: To assess fetal anatomy and detect a broader range of potential fetal abnormalities and conditions.
3. Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT):
NIPT is a newer type of screening that analyzes cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) circulating in the mother's blood. It can detect chromosomal abnormalities like Trisomy 21, Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome), and Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome), as well as certain sex chromosome abnormalities.
Main Goal: To provide a highly accurate screening test for chromosomal abnormalities with minimal risk to the fetus.
4. Specialized Screening Tests:
Depending on the individual circumstances and risk factors, other specialized screening tests might be recommended, such as:
- Carrier screening: Identifies if parents carry genes for recessive disorders that could affect their child.
- Anomaly scans: Detailed ultrasounds to assess fetal anatomy for potential structural abnormalities.
- Genetic testing: More invasive tests (like amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling) that directly analyze fetal DNA to confirm or rule out specific conditions.
Beyond Detection: Addressing Ethical Considerations
While the primary goal is informed decision-making, prenatal screening raises complex ethical considerations:
- The potential for psychological distress: Receiving a positive screening result can be emotionally challenging for parents. Counseling and support are crucial components of the screening process.
- The possibility of false positives and false negatives: Screening tests are not diagnostic; a positive result doesn't guarantee the presence of a condition, and a negative result doesn't guarantee its absence. This uncertainty can create anxiety and stress.
- Reproductive choices: Screening results often lead to difficult decisions about whether to continue or terminate the pregnancy. Accessing unbiased genetic counseling is crucial in making these choices.
- Discrimination and stigma: Prenatal screening can sometimes lead to discrimination or stigmatization of individuals with disabilities. Promoting inclusivity and understanding is crucial in countering these harmful effects.
The Importance of Genetic Counseling
Genetic counseling plays a vital role in the prenatal screening process. Genetic counselors help parents understand:
- The implications of the screening results: They interpret the results and explain the probabilities and limitations of the tests.
- The risks and benefits of further diagnostic tests: They discuss the potential risks associated with invasive procedures and help parents make informed choices.
- Available support resources: They provide information on support groups, medical specialists, and other resources to help parents cope with the information received.
- Ethical considerations and personal values: They guide parents through the ethical and personal aspects of decision-making regarding pregnancy continuation or termination.
Conclusion: Empowering Parents, Improving Outcomes
The main goal of prenatal screening is to empower expectant parents with the information they need to make informed decisions about their pregnancy. This involves identifying potential risks, seeking specialized care, choosing appropriate management strategies, and reducing anxiety and uncertainty. While screening tests have limitations and raise ethical considerations, their crucial role in promoting maternal and child health cannot be understated. Through responsible use and appropriate counseling, prenatal screening contributes significantly to improved pregnancy outcomes and enhances the well-being of families worldwide. The focus remains on providing information to support parents, not simply identifying problems, helping them navigate the complexities of pregnancy with confidence and understanding. The responsible use of prenatal screening ultimately leads to better care, healthier outcomes, and more informed choices for expectant families. This sophisticated process, therefore, should always be approached with sensitivity, respect, and a commitment to evidence-based best practices in obstetrics and genetic counseling.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Best Describes The Terrorist Planning Cycle
Mar 18, 2025
-
Cdl Combination Test Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
Life Insurance Exam Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Direct Carry Is Used To Transfer A Patient
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Emancipation Proclamation Of January 1 1863 Quizlet
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Main Goal Of Prenatal Screening Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
