When A Child Experiences A Blunt Chest Injury Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
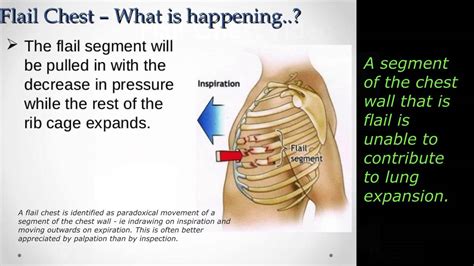
Table of Contents
When a Child Experiences a Blunt Chest Injury: A Comprehensive Guide
Blunt chest trauma in children is a serious medical condition requiring immediate attention. Unlike adults, children's chests are more pliable and their ribs are more flexible, leading to different injury patterns and potential complications. Understanding the mechanisms of injury, potential consequences, and appropriate management is crucial for healthcare professionals and caregivers alike. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of blunt chest injuries in children, examining various aspects from diagnosis to long-term implications.
Understanding Blunt Chest Trauma in Children
What constitutes blunt chest trauma? Blunt chest trauma refers to injuries to the chest caused by a force that doesn't penetrate the skin, such as a car accident, fall, sports injury, or assault. The impact can cause damage to various structures within the chest, including the ribs, sternum, lungs, heart, great vessels, and diaphragm.
Why are children more vulnerable? Children's chests are less rigid than adults', with more flexible ribs and cartilage. This flexibility can lead to paradoxical breathing (parts of the chest moving in opposite directions during breathing) and flail chest (multiple rib fractures causing unstable chest wall segments) less frequently than in adults, but with potentially serious consequences. Their developing organs are also more susceptible to damage.
Mechanisms of Injury and Common Injuries
Several mechanisms can cause blunt chest trauma in children. These include:
- Motor vehicle collisions: This is a leading cause, with children often sustaining injuries from impact forces and restraint systems (or lack thereof).
- Falls: Falls from heights, whether from playground equipment, trees, or buildings, can result in significant chest injuries.
- Sports injuries: Contact sports, such as football and hockey, increase the risk of blunt chest trauma.
- Child abuse: Blunt force trauma to the chest can be a sign of physical abuse, requiring careful evaluation and reporting.
- Bicycle accidents: Collisions or falls from bicycles can lead to chest injuries, particularly if the child isn't wearing a helmet.
Common types of blunt chest injuries in children include:
- Rib fractures: Rib fractures are common, particularly in older children. While often healing spontaneously, they can lead to pain, respiratory distress, and pneumothorax (collapsed lung).
- Sternal fractures: Fractures of the breastbone are less common but can be severe, potentially causing damage to underlying structures.
- Pneumothorax: A collapsed lung occurs when air enters the pleural space (space between the lung and chest wall), causing the lung to collapse. This is a life-threatening condition requiring immediate medical intervention.
- Hemothorax: A collection of blood in the pleural space, also requiring urgent attention.
- Cardiac contusion: Bruising of the heart muscle can lead to irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias) and heart failure.
- Aortic injury: Damage to the aorta, the largest artery in the body, is a life-threatening emergency.
- Diaphragmatic rupture: A tear in the diaphragm can allow abdominal organs to herniate into the chest cavity.
- Tracheobronchial injury: Injury to the trachea or bronchi (airways) can cause respiratory distress.
Assessment and Diagnosis of Blunt Chest Injuries in Children
Prompt and thorough assessment is paramount in managing blunt chest injuries in children. This involves a systematic approach, integrating history, physical examination, and imaging studies.
Initial Assessment: ABCDE Approach
The initial assessment follows the ABCDE approach:
- Airway: Assess for airway patency, ensuring a clear and unobstructed airway. Look for signs of respiratory distress, such as increased respiratory rate, retractions (indrawing of the chest wall during breathing), and nasal flaring.
- Breathing: Assess respiratory rate, rhythm, and depth. Listen for breath sounds, checking for the presence of diminished or absent breath sounds, which may indicate pneumothorax or hemothorax. Observe for paradoxical chest movement or flail chest.
- Circulation: Assess heart rate, rhythm, and blood pressure. Check for signs of shock (pale skin, rapid weak pulse, low blood pressure).
- Disability: Assess neurological status, including level of consciousness and pupillary response.
- Exposure: Completely expose the child to allow for a thorough physical examination.
Diagnostic Tests
Several diagnostic tests may be used to confirm and characterize blunt chest injuries:
- Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray is essential for identifying pneumothorax, hemothorax, rib fractures, sternal fractures, and other abnormalities.
- Computed tomography (CT) scan: A CT scan provides detailed images of the chest, allowing for a more precise assessment of injuries, including those involving the heart, great vessels, and diaphragm.
- Echocardiography: An echocardiogram uses ultrasound to assess the heart's structure and function, helping identify cardiac contusions and other cardiac injuries.
- Ultrasound: Focused assessment with sonography for trauma (FAST) examination uses ultrasound to rapidly assess for free fluid in the abdomen and chest, suggesting internal bleeding.
Management and Treatment of Blunt Chest Injuries in Children
Management depends on the severity and nature of the injuries. Some injuries may require conservative management, while others necessitate immediate surgical intervention.
Conservative Management
Conservative management may include:
- Pain management: Analgesics (pain relievers) may be necessary to manage rib pain.
- Oxygen therapy: Supplemental oxygen may be provided to improve oxygenation.
- Respiratory support: In cases of severe respiratory distress, mechanical ventilation may be required.
- Observation: Close monitoring of vital signs and respiratory status is crucial.
Surgical Intervention
Surgical intervention may be required for life-threatening injuries:
- Chest tube placement: A chest tube is inserted to drain air or blood from the pleural space in cases of pneumothorax or hemothorax.
- Open thoracotomy: Open chest surgery may be necessary to repair major injuries such as diaphragmatic rupture or vascular injuries.
- Cardiothoracic surgery: Cardiac surgery may be required for cardiac contusions or injuries to the great vessels.
Long-Term Implications and Rehabilitation
Following blunt chest trauma, children may experience long-term implications. These can include:
- Chronic pain: Persistent pain may occur, particularly with rib fractures.
- Respiratory problems: Some children may develop chronic lung conditions.
- Cardiac complications: Cardiac arrhythmias or heart failure may develop in some cases.
- Psychological impact: The trauma can lead to anxiety, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and other psychological problems.
Rehabilitation may involve:
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help improve respiratory function, strength, and mobility.
- Pain management: Ongoing pain management strategies may be needed.
- Psychological counseling: Counseling can help address psychological issues.
Prevention of Blunt Chest Injuries in Children
Preventing blunt chest injuries requires a multi-pronged approach:
- Car seat safety: Proper use of age-appropriate car seats is crucial.
- Helmet use: Helmet use is recommended for children participating in activities such as cycling, skateboarding, and riding scooters.
- Supervision: Close supervision of children, particularly during activities that carry a risk of falls, is important.
- Injury-proofing homes: Making homes safe for children by removing potential hazards can help reduce the risk of falls and other injuries.
- Education: Educating parents and caregivers about the risks of blunt chest trauma and appropriate safety measures can contribute to prevention.
Conclusion
Blunt chest trauma in children is a potentially life-threatening condition requiring prompt assessment and management. The unique anatomical and physiological characteristics of children necessitate a tailored approach to diagnosis and treatment. Early intervention and appropriate management significantly impact outcomes, emphasizing the importance of awareness and prompt medical attention. Understanding the mechanisms of injury, potential complications, and long-term implications enables healthcare professionals and caregivers to provide optimal care and support. Furthermore, a proactive approach towards prevention, through education and safety measures, plays a crucial role in reducing the incidence of this serious injury. The information provided here should not substitute for professional medical advice; always consult with a healthcare provider for any concerns about a child's health.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
True Or False Professional And Technical Communication Is Research Oriented
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Best Describes The Terrorist Planning Cycle
Mar 18, 2025
-
Cdl Combination Test Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
Life Insurance Exam Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Direct Carry Is Used To Transfer A Patient
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about When A Child Experiences A Blunt Chest Injury Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
