Which Of The Following Is Not A Greenhouse Gas Quizlet
Breaking News Today
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
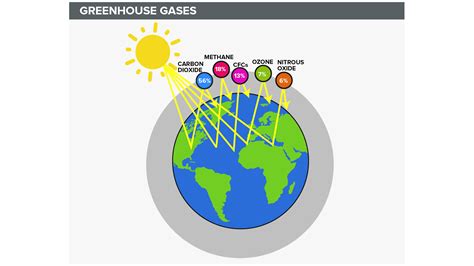
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is NOT a Greenhouse Gas? A Deep Dive into Atmospheric Composition and Climate Change
The Earth's atmosphere is a complex mixture of gases, some of which play a crucial role in regulating our planet's temperature. Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are components of the atmosphere that trap heat and warm the planet. Understanding which gases contribute to this warming effect, and which do not, is essential for comprehending climate change and developing effective mitigation strategies. This comprehensive guide will explore the key greenhouse gases and definitively answer the question: which of the following is NOT a greenhouse gas? We'll delve into the scientific principles behind the greenhouse effect, examine the properties of various atmospheric constituents, and provide clear examples to solidify your understanding.
What are Greenhouse Gases?
Before identifying the non-greenhouse gas, let's define what constitutes a greenhouse gas. Greenhouse gases are molecules that absorb and re-emit infrared radiation (heat) radiated from the Earth's surface. This process traps heat within the atmosphere, creating a warming effect known as the greenhouse effect. This effect is crucial for life on Earth; without it, our planet would be significantly colder and uninhabitable. However, human activities have increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, leading to an enhanced greenhouse effect and global warming.
Key Greenhouse Gases:
Several gases contribute significantly to the greenhouse effect. The most important ones include:
-
Carbon Dioxide (CO2): This is the primary greenhouse gas produced by human activities, primarily through the burning of fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) for energy, deforestation, and industrial processes. CO2 is a particularly potent greenhouse gas due to its abundance and long atmospheric lifetime.
-
Methane (CH4): Methane is a much more potent greenhouse gas than CO2, trapping significantly more heat per molecule. Its main sources include agriculture (livestock, rice paddies), natural gas leaks, landfills, and wastewater treatment. While its atmospheric lifetime is shorter than CO2, its high warming potential makes it a significant concern.
-
Nitrous Oxide (N2O): Nitrous oxide is another powerful greenhouse gas released from various sources, including agricultural activities (fertilizers), industrial processes, and the burning of fossil fuels. It has a very long atmospheric lifetime, making it a long-term contributor to global warming.
-
Fluorinated Gases: This group includes hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), and nitrogen trifluoride (NF3). These are synthetic gases used in various industrial applications, such as refrigeration, air conditioning, and electronics manufacturing. While present in much smaller concentrations than CO2, they possess extremely high global warming potentials, making them significant contributors to climate change on a per-molecule basis. They are often referred to as high-global warming potential (GWP) gases.
Gases that are NOT Greenhouse Gases:
Now, let's address the central question of this article. Many gases in the atmosphere do not absorb and re-emit infrared radiation effectively. Therefore, they do not significantly contribute to the greenhouse effect. The most prominent example is:
- Nitrogen (N2): Nitrogen constitutes about 78% of the Earth's atmosphere. Its molecular structure is symmetrical and doesn't interact strongly with infrared radiation. This means it doesn't absorb and re-emit heat effectively, making it a negligible contributor to the greenhouse effect.
Other Gases with Minimal Greenhouse Effect:
While nitrogen is the most abundant example, several other gases exhibit minimal greenhouse effects:
-
Oxygen (O2): Oxygen, making up approximately 21% of the atmosphere, similarly lacks the molecular properties needed to absorb infrared radiation efficiently. Its contribution to the greenhouse effect is minimal.
-
Argon (Ar): Argon is an inert noble gas comprising about 1% of the atmosphere. Like nitrogen and oxygen, its molecular structure prevents it from significantly interacting with infrared radiation.
Why the Distinction Matters:
Understanding which gases are and are not greenhouse gases is crucial for several reasons:
-
Climate Change Modeling: Accurate climate models require a comprehensive understanding of the radiative properties of all atmospheric components. Knowing which gases contribute to the greenhouse effect allows for more precise predictions of future climate change.
-
Mitigation Strategies: Focusing mitigation efforts on reducing the emissions of potent greenhouse gases, like CO2, CH4, and N2O, is essential for combating global warming. Understanding which gases are not significant contributors helps prioritize these efforts.
-
Policy Development: Effective climate policies rely on accurate scientific information about greenhouse gases and their impact on the environment. Identifying and quantifying the contribution of different gases is vital for designing policies that address the climate crisis effectively.
Quizlet-Style Questions and Answers:
To further solidify your understanding, let's explore some quizlet-style questions and answers:
Q1: Which of the following is NOT a greenhouse gas? (a) Carbon Dioxide (CO2) (b) Methane (CH4) (c) Nitrogen (N2) (d) Nitrous Oxide (N2O)
A1: (c) Nitrogen (N2)
Q2: Which gas is the most abundant in the Earth's atmosphere but has a negligible effect on the greenhouse effect? (a) Oxygen (O2) (b) Carbon Dioxide (CO2) (c) Nitrogen (N2) (d) Methane (CH4)
A2: (c) Nitrogen (N2)
Q3: What is the primary reason why nitrogen gas (N2) does not contribute significantly to the greenhouse effect? (a) Its low concentration in the atmosphere. (b) Its symmetrical molecular structure. (c) Its high reactivity. (d) Its low molecular weight.
A3: (b) Its symmetrical molecular structure.
Q4: Which group of gases has extremely high global warming potentials, even though their atmospheric concentrations are relatively low? (a) Noble Gases (b) Fluorinated Gases (c) Oxygen and Nitrogen (d) Ozone-depleting substances
A4: (b) Fluorinated Gases
Q5: The enhanced greenhouse effect, leading to global warming, is primarily caused by: (a) Natural variations in solar radiation. (b) Increased concentrations of greenhouse gases due to human activities. (c) Volcanic eruptions. (d) Changes in Earth's orbit.
A5: (b) Increased concentrations of greenhouse gases due to human activities.
Conclusion:
Understanding the properties of atmospheric gases and their contribution to the greenhouse effect is crucial for comprehending climate change. While many gases are involved, it's clear that some, like nitrogen, oxygen and argon, play a negligible role in warming the planet. Focusing on reducing emissions of significant greenhouse gases remains paramount in addressing this critical global challenge. By accurately identifying and quantifying the impact of various atmospheric constituents, we can develop more effective mitigation strategies and work towards a sustainable future. This knowledge empowers informed decision-making on a personal, community, and global level, enabling us to make a positive impact on climate change.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
True Or False Professional And Technical Communication Is Research Oriented
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Best Describes The Terrorist Planning Cycle
Mar 18, 2025
-
Cdl Combination Test Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
Life Insurance Exam Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Direct Carry Is Used To Transfer A Patient
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is Not A Greenhouse Gas Quizlet . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
