Which Of The Following Is True About Data Collection
Breaking News Today
Mar 20, 2025 · 7 min read
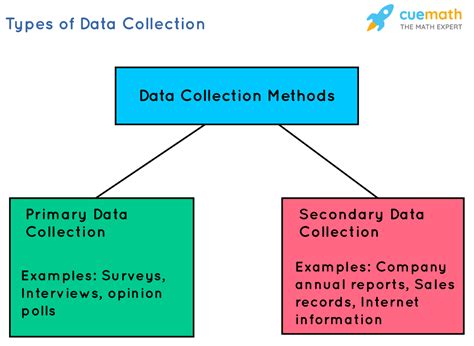
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is True About Data Collection? A Deep Dive into Data Integrity and Best Practices
Data collection is the cornerstone of any successful research project, business strategy, or technological advancement. From understanding consumer behavior to developing life-saving medical treatments, the ability to collect, analyze, and interpret data accurately is paramount. But what exactly is true about data collection? This comprehensive guide will explore the nuances of data collection, addressing common misconceptions and outlining best practices to ensure data integrity and reliable results. We'll delve into various data collection methods, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses, and ultimately provide you with a robust understanding of this crucial process.
Understanding the Fundamentals of Data Collection
Before we tackle the "which of the following is true" question, let's lay a solid foundation. Data collection, at its core, is the systematic process of gathering and measuring information on targeted variables in an established system, to determine the strength of the relationships between variables. This seemingly simple definition encompasses a vast array of methodologies and considerations. Crucially, effective data collection requires careful planning and execution to avoid bias and ensure the accuracy and reliability of the collected information.
Key Aspects of Effective Data Collection:
-
Clearly Defined Objectives: What are you hoping to achieve with your data collection? Defining clear, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) objectives is crucial. This provides a roadmap for the entire process, guiding your choice of methods and analysis.
-
Target Population Identification: Who is your data going to be collected from? Accurately identifying your target population is critical for obtaining meaningful results. Understanding the characteristics of this group will influence your sampling strategy.
-
Choosing the Right Methodology: There's no one-size-fits-all approach to data collection. The best method depends on your research questions, resources, and target population. We'll explore various methods in detail later.
-
Data Quality Assurance: Implementing robust quality control measures throughout the data collection process is essential. This includes validating data entries, checking for inconsistencies, and addressing missing data.
-
Ethical Considerations: Ethical considerations are paramount. This includes obtaining informed consent from participants, ensuring data anonymity and confidentiality, and adhering to all relevant legal and ethical guidelines.
Common Data Collection Methods: A Comparative Analysis
Numerous methods exist for collecting data, each with its own strengths and limitations. Understanding these differences is essential for selecting the appropriate technique for your specific needs.
1. Surveys:
-
Description: Surveys are structured questionnaires that gather information from a large number of participants. They can be administered via various methods, including online platforms, paper forms, or telephone interviews.
-
Strengths: Cost-effective for large-scale data collection; easy to administer and analyze; allows for a wide range of question types.
-
Weaknesses: Can suffer from low response rates; susceptible to response bias; may not capture nuanced information.
2. Interviews:
-
Description: Interviews involve direct interaction between the researcher and participant, allowing for in-depth exploration of topics. They can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured.
-
Strengths: Provides rich qualitative data; allows for clarification and follow-up questions; can build rapport with participants.
-
Weaknesses: Time-consuming and expensive; susceptible to interviewer bias; difficult to analyze large amounts of data.
3. Observations:
-
Description: Observations involve systematically watching and recording behavior in a natural setting or controlled environment.
-
Strengths: Provides firsthand data on behavior; less susceptible to response bias; can capture nonverbal cues.
-
Weaknesses: Can be time-consuming and resource-intensive; observer bias can be a significant concern; ethical considerations regarding privacy need careful attention.
4. Experiments:
-
Description: Experiments involve manipulating one or more variables to determine their effect on another variable. They allow for causal inferences.
-
Strengths: Can establish cause-and-effect relationships; high degree of control over variables.
-
Weaknesses: Can be expensive and time-consuming; may not be feasible or ethical in all situations; artificial settings may not reflect real-world scenarios.
5. Document Analysis:
-
Description: Involves examining existing documents such as reports, records, or articles to extract relevant information.
-
Strengths: Cost-effective; allows access to a large amount of data; can provide historical context.
-
Weaknesses: Data may be incomplete or unreliable; may not be representative of the population of interest; requires careful interpretation.
Addressing Common Misconceptions About Data Collection
Many misconceptions surround data collection, potentially leading to flawed research and inaccurate conclusions. Let's address some of the most prevalent:
Myth 1: More Data is Always Better
While having a large dataset can be beneficial, it's not always the case. The quality of data is far more important than quantity. A small, high-quality dataset can yield more valuable insights than a large, poorly collected dataset filled with errors and biases. Focus on data quality and reliability over sheer volume.
Myth 2: One Method Fits All
As discussed earlier, different data collection methods are suitable for different research questions and contexts. Choosing the wrong method can lead to inaccurate or incomplete data. Careful consideration of your research objectives and target population is crucial for selecting the most appropriate method.
Myth 3: Data Cleaning is Unnecessary
Data cleaning, the process of identifying and correcting errors and inconsistencies in a dataset, is an essential step in data analysis. Failing to clean your data can lead to inaccurate conclusions and misleading results. Allocate sufficient time and resources to data cleaning to ensure data integrity.
Myth 4: Technology Solves All Data Collection Problems
While technology can significantly enhance data collection, it's not a panacea. Technological tools are only as good as the design and implementation behind them. Careful planning, consideration of ethical implications, and robust quality control measures are still crucial, regardless of the technology used.
Which of the Following is True About Data Collection? Examples and Answers
Now, let's address the core question of the article. To illustrate, we'll present a few multiple-choice questions and provide detailed explanations of the correct answers.
Question 1:
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding data collection methods?
a) Surveys are always the most efficient method for gathering large amounts of data. b) Interviews are superior to surveys for collecting quantitative data. c) The choice of data collection method depends on the research question and resources available. d) Observations are only useful for studying overt behaviors, not attitudes or beliefs.
Answer: c) The choice of data collection method depends on the research question and resources available.
Explanation: While surveys can be efficient for large-scale data collection, they are not always the best method. Interviews are better suited for in-depth qualitative data, while observations can capture both behaviors and contextual information. The best method is always context-dependent.
Question 2:
What is a critical aspect of ensuring data quality during the data collection process?
a) Minimizing the number of participants to reduce data analysis time. b) Implementing robust quality control measures, including data validation and error checking. c) Relying solely on automated data entry to minimize human error. d) Ignoring missing data, as it represents a small percentage of the overall dataset.
Answer: b) Implementing robust quality control measures, including data validation and error checking.
Explanation: Data quality is paramount. Minimizing participants can limit generalizability, automated entry can still have errors, and ignoring missing data can lead to biased results. Thorough quality control, including validation and error checking, is essential.
Question 3:
Which ethical consideration is MOST important during data collection?
a) Ensuring the researcher's personal beliefs don't influence the results. b) Obtaining informed consent from participants and maintaining data confidentiality. c) Using only readily available, publicly accessible data sources. d) Selecting participants based on convenience rather than representative sampling.
Answer: b) Obtaining informed consent from participants and maintaining data confidentiality.
Explanation: Ethical considerations are fundamental. While researcher bias is important, informed consent and data confidentiality are paramount to protect participant rights and privacy. Convenience sampling and reliance solely on public data can limit the study's scope and impact.
Question 4:
Which of the following is NOT a common method of data collection?
a) Surveys b) Interviews c) Experiments d) Telepathy
Answer: d) Telepathy
Explanation: Surveys, interviews, and experiments are established and widely used data collection methods. Telepathy, the purported transmission of information from one mind to another without using known senses, is not a scientifically validated or reliable data collection method.
Conclusion: The Importance of Rigorous Data Collection
Data collection is not a simple process; it's a meticulous undertaking requiring careful planning, execution, and attention to detail. Understanding the various methods available, their strengths and weaknesses, and the importance of data integrity and ethical considerations is crucial for generating meaningful and reliable results. By avoiding common misconceptions and adhering to best practices, researchers and businesses can ensure the accuracy and validity of their data, leading to more informed decisions and impactful outcomes. Remember, the pursuit of knowledge and informed decision-making hinges on the quality of data we collect. Embrace rigor, prioritize ethical considerations, and strive for excellence in your data collection endeavors.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Match The Situation With The Appropriate Use Of Network Media
Mar 21, 2025
-
Unused Live Ammunition Should Be Inventoried And Then
Mar 21, 2025
-
Obligations That Are Due Within One Year Are
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is The Definition Of Freezing Your Credit Everfi
Mar 21, 2025
-
Jose 1 Of 1 En La Biblioteca
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is True About Data Collection . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
