Which Of The Following Is True About Half-duplex Mode
Breaking News Today
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
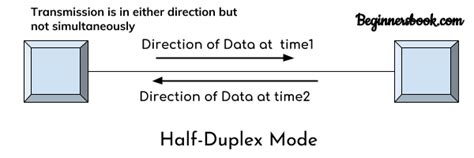
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is True About Half-Duplex Mode? A Deep Dive into Communication Protocols
Half-duplex communication is a method of data transmission where data can travel in both directions, but only one direction at a time. Understanding its nuances is crucial for anyone working with networking, communication systems, or even embedded systems. This article delves deep into half-duplex mode, exploring its characteristics, comparing it to full-duplex, examining its use cases, and addressing common misconceptions. We'll answer the question, "Which of the following is true about half-duplex mode?" by comprehensively exploring its nature.
Understanding Half-Duplex Communication
In half-duplex mode, only one device can transmit data at a time. Think of it like a walkie-talkie: one person speaks while the other listens; to respond, the listener must wait for the speaker to finish before transmitting their message. This inherent limitation introduces a critical concept: collision. If two devices attempt to transmit simultaneously, a collision occurs, resulting in data corruption and the need for retransmission.
This contrasts sharply with full-duplex communication, where data can flow in both directions simultaneously. Think of a telephone conversation: both parties can speak and listen at the same time without interruption. Full-duplex is significantly more efficient for high-bandwidth applications.
Key Characteristics of Half-Duplex:
- One-way transmission at a time: Only one device can transmit while others listen.
- Carrier sense multiple access with collision detection (CSMA/CD): This is a common access method used in half-duplex networks. Devices listen to the network before transmitting to avoid collisions. If a collision is detected, a backoff mechanism is employed before retransmission.
- Lower bandwidth efficiency: Due to the limitations of single-direction transmission, the overall throughput is lower compared to full-duplex.
- Simpler implementation: Historically, half-duplex was simpler to implement and required less complex hardware compared to full-duplex.
- Susceptible to collisions: The inherent risk of data corruption due to simultaneous transmissions is a significant drawback.
- Suitable for low-bandwidth applications: Its simplicity and low cost make it suitable for applications where high bandwidth is not a critical requirement.
Half-Duplex vs. Full-Duplex: A Detailed Comparison
The fundamental difference lies in the directionality of data transmission. Let's break down the key differences between half-duplex and full-duplex communication:
| Feature | Half-Duplex | Full-Duplex |
|---|---|---|
| Data Flow | One direction at a time | Bi-directional simultaneously |
| Efficiency | Lower | Higher |
| Collisions | Prone to collisions | No collisions |
| Complexity | Simpler implementation | More complex implementation |
| Cost | Typically lower | Typically higher |
| Bandwidth | Suitable for low-bandwidth applications | Suitable for high-bandwidth applications |
| Example | Walkie-talkie, early Ethernet networks | Telephone conversation, modern Ethernet (using switches) |
| Collision Detection | Often uses CSMA/CD | Not needed |
| Protocols | Older Ethernet protocols, some wireless protocols | Gigabit Ethernet, most modern wireless protocols |
Examples of Half-Duplex Communication
While less prevalent in modern high-speed networks, half-duplex communication still finds application in specific contexts:
- Older Ethernet Networks (using hubs): Early Ethernet networks used hubs, which operate in half-duplex mode. All devices on the network shared the same communication channel, leading to potential collisions.
- Some Wireless Protocols: Certain wireless communication protocols, especially older ones, might operate in half-duplex mode. They might use techniques like CSMA/CA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance) to reduce collisions.
- Walkie-talkies: The classic example of half-duplex communication. Only one person can speak at a time.
- Simple Serial Communication: In some embedded systems or low-speed communication scenarios, half-duplex communication might be employed due to its simplicity.
- Citizen's Band (CB) Radio: Similar to walkie-talkies, CB radios operate in half-duplex mode.
CSMA/CD: The Heart of Half-Duplex Collision Handling
Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) is a crucial protocol used in half-duplex networks to manage collisions. Here's how it works:
- Carrier Sense: Before transmitting, a device listens to the network to check if the channel is busy.
- Multiple Access: Multiple devices can share the same channel.
- Collision Detection: If two devices transmit simultaneously, a collision occurs. Both devices detect this collision.
- Backoff Algorithm: After detecting a collision, devices use a randomized backoff algorithm to delay their retransmission. This helps to avoid repeated collisions.
- Retransmission: After the backoff period, the devices attempt to retransmit their data.
This process continues until the data is successfully transmitted. The efficiency of CSMA/CD depends on the network load and the effectiveness of the backoff algorithm.
Addressing Common Misconceptions about Half-Duplex
Several misconceptions often surround half-duplex communication:
- Myth: Half-duplex is inherently slow. While half-duplex has lower potential bandwidth than full-duplex, its speed is not solely determined by the mode. The speed of the underlying physical medium plays a significant role.
- Myth: Half-duplex is always outdated. Half-duplex is still relevant in specific niche applications where its simplicity and lower cost outweigh the need for high bandwidth.
- Myth: Half-duplex is always unreliable. While more susceptible to collisions, proper implementation and use of protocols like CSMA/CD can mitigate reliability issues.
The Future of Half-Duplex
While full-duplex communication is becoming increasingly prevalent, half-duplex still holds a place, primarily in scenarios where cost and simplicity are prioritized over high bandwidth. The continued development and optimization of protocols like CSMA/CD could improve the efficiency and reliability of half-duplex communication in these niche applications. However, for high-bandwidth, low-latency applications, full-duplex will likely remain the dominant technology.
Conclusion: Which of the Following is True About Half-Duplex Mode?
Now, let's revisit the initial question, "Which of the following is true about half-duplex mode?" Based on our exploration, several statements could be true depending on the specific context. However, generally speaking, the following statements would accurately reflect the nature of half-duplex communication:
- Only one device can transmit at a time. This is the defining characteristic of half-duplex.
- It is more susceptible to collisions than full-duplex. Simultaneous transmission attempts lead to data corruption.
- It is generally less efficient than full-duplex. The inability to transmit simultaneously limits overall throughput.
- It often uses CSMA/CD for collision detection and management. This protocol is crucial for mitigating collision issues.
- It is simpler to implement than full-duplex. This explains its prevalence in low-cost, low-bandwidth applications.
Understanding the nuances of half-duplex communication is essential for anyone working with networks and communication systems. By grasping its characteristics, limitations, and use cases, you can make informed decisions about the appropriate communication mode for your specific application. Remember to weigh the trade-offs between simplicity, cost, and bandwidth efficiency when choosing between half-duplex and full-duplex.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
True Or False Professional And Technical Communication Is Research Oriented
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Best Describes The Terrorist Planning Cycle
Mar 18, 2025
-
Cdl Combination Test Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
Life Insurance Exam Questions And Answers Pdf
Mar 18, 2025
-
The Direct Carry Is Used To Transfer A Patient
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is True About Half-duplex Mode . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
