Which Statement About Reserved Powers Is Accurate
Breaking News Today
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
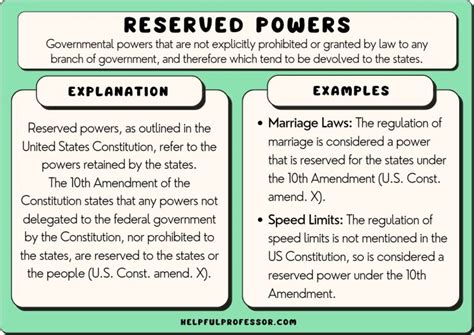
Table of Contents
Which Statement About Reserved Powers Is Accurate? Delving into the Complexities of Federalism
The concept of "reserved powers" lies at the heart of federal systems, shaping the intricate balance between a central government and its constituent units. Understanding reserved powers is crucial to grasping the dynamics of power distribution and the limitations imposed on both federal and state authorities. This article will dissect the complexities surrounding reserved powers, explore common misconceptions, and ultimately determine which statement about them is most accurate. We'll examine various interpretations and contextual factors impacting the application of reserved powers in different federal systems.
Understanding Reserved Powers: A Foundational Concept
Reserved powers, also known as residual powers, are governmental powers that are neither prohibited nor explicitly given to the federal government by a constitution. These powers are implicitly reserved for the states or other sub-national entities. The exact allocation of reserved powers varies significantly depending on the specific structure of the federal system in question. The principle underlying reserved powers is that all powers not specifically delegated to the federal government remain within the jurisdiction of the states or regions.
This principle is fundamental to maintaining a balance of power and preventing the centralization of authority. It allows states to retain control over matters deemed crucial to their unique identities and needs, preventing a homogenous, potentially oppressive, national policy across diverse regions.
The Tenth Amendment: A Cornerstone of Reserved Powers in the US
In the United States, the Tenth Amendment to the Constitution explicitly addresses the concept of reserved powers: "The powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people." This amendment serves as a constitutional cornerstone for the allocation of power between the federal government and the individual states.
However, interpreting the Tenth Amendment's implications has been a continuous source of legal and political debate throughout American history. The Supreme Court's interpretation of the amendment has evolved over time, influencing the scope and application of reserved powers. The balance between federal and state authority remains a dynamic and contested area of American jurisprudence.
Common Misconceptions Regarding Reserved Powers
Several misconceptions surround the concept of reserved powers, leading to confusion and inaccurate understandings of their role in federal systems:
Misconception 1: Reserved Powers are Absolute and Unchallengeable
False. While reserved powers grant substantial autonomy to states, they are not entirely without limits. The federal government may still exert influence through various means, such as through the use of its spending power (e.g., attaching conditions to federal grants) or through the interpretation and application of the Commerce Clause. Court rulings frequently redefine the boundaries between federal and state authority, demonstrating that reserved powers are subject to ongoing legal interpretation and challenge.
Misconception 2: Reserved Powers are Identical Across All Federal Systems
False. The specific distribution of reserved powers differs significantly depending on the constitutional structure of each federal system. The Canadian federal system, for example, operates under a different framework than the American system, resulting in varying allocations of power between the federal and provincial governments. Similarly, the Australian system features its own unique balance of power between the federal and state governments. These variations highlight the inherent flexibility and adaptability of the concept of reserved powers depending on the specific context.
Misconception 3: Reserved Powers are Static and Unchanging
False. The practical application of reserved powers is not static; it's subject to change over time due to judicial interpretations, legislative actions, and evolving societal norms. As societies evolve and new challenges emerge, the lines between federal and state responsibilities may shift, necessitating reinterpretations of reserved powers to align with contemporary needs and values.
Accurate Statements About Reserved Powers: Refining the Understanding
Given the complexities and nuances, several statements can accurately describe aspects of reserved powers. However, one statement captures the essence more comprehensively than others:
"Reserved powers are those governmental powers not explicitly granted to the federal government and implicitly retained by the states or other sub-national entities, subject to ongoing legal interpretation and potential limitations imposed by federal legislation or judicial review."
This statement effectively captures several key elements:
- Implicit Retention: It accurately reflects that reserved powers are not explicitly listed but are derived from the principle of not delegating powers to the central government.
- State/Sub-National Jurisdiction: It clearly identifies the entities that retain these powers.
- Legal Interpretation: It acknowledges the continuous process of legal interpretation that shapes the scope and application of these powers.
- Federal Limitations: It recognizes the limits placed on reserved powers through federal actions and judicial decisions.
Case Studies: Examining Reserved Powers in Action
To further illuminate the concept, let's analyze how reserved powers have played out in different contexts:
United States: The Ongoing Debate Over Healthcare
The Affordable Care Act (ACA) sparked significant debate regarding the balance of power between the federal government and the states. The ACA involved the federal government significantly influencing the healthcare landscape, raising questions about potential encroachment on state-reserved powers related to healthcare policy and regulation. Court challenges to the ACA underscored the ongoing tension between federal authority and states' rights to manage their own healthcare systems.
Canada: Provincial Jurisdiction over Education
In Canada, education falls primarily under the jurisdiction of the provinces, reflecting a significant aspect of their reserved powers. This means provincial governments have significant control over curriculum development, teacher training, and funding allocation for educational institutions within their respective territories. While the federal government plays a supporting role through funding initiatives, the core authority resides with the provinces, exemplifying the operational principle of reserved powers.
Australia: State Control over Natural Resources
Australia's federal system grants substantial control over natural resources to individual states. This includes matters such as mining regulations, environmental protection related to resource extraction, and the management of natural resource revenue. The state-level authority over these resources highlights the application of reserved powers and the state's role in managing resources vital to their economy and environment.
Conclusion: Navigating the Nuances of Reserved Powers
Reserved powers represent a crucial aspect of federalism, safeguarding the autonomy of states and preventing the over-centralization of power. Understanding their complexities, including the inherent limitations and the ongoing legal interpretations, is crucial to comprehending the dynamics of power allocation in federal systems. While the specific distribution and application of reserved powers vary considerably across different countries, the underlying principle of retaining power not explicitly delegated to the federal government remains central to the operation of successful federal systems. The accuracy of any statement about reserved powers hinges on acknowledging this nuanced interplay of implicit authority, legal evolution, and the potential for both state and federal influence. Ongoing legal and political debates surrounding reserved powers underscore their enduring significance in shaping the balance of power within federal states.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Company That Sells Baby Food Is Interested
Mar 13, 2025
-
How Does The Wordplay In These Lines Affect The Mood
Mar 13, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Best Describes Spyware
Mar 13, 2025
-
The Objective Of Inventory Management Is To
Mar 13, 2025
-
Tina Jones Comprehensive Assessment Shadow Health Answers
Mar 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Statement About Reserved Powers Is Accurate . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
