Which Statement Is Consistent With The Law Of Supply
Breaking News Today
Mar 27, 2025 · 6 min read
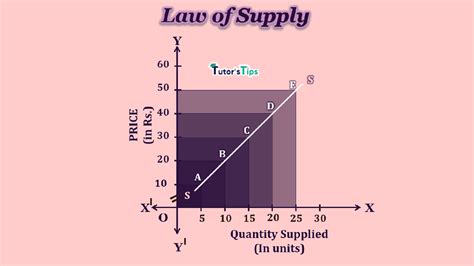
Table of Contents
Which Statement is Consistent with the Law of Supply?
The law of supply is a fundamental principle in economics that describes the relationship between the price of a good or service and the quantity supplied. Understanding this law is crucial for anyone involved in business, economics, or simply trying to make sense of market dynamics. This article will delve deep into the law of supply, exploring its core tenets, providing examples of statements consistent with it, and debunking common misconceptions. We'll also examine how external factors can influence the supply curve and its implications for businesses and consumers.
Understanding the Law of Supply
The law of supply states that, all other factors being equal (ceteris paribus), as the price of a good or service increases, the quantity supplied of that good or service will also increase. Conversely, as the price decreases, the quantity supplied will decrease. This relationship is positive, meaning the variables move in the same direction.
It's crucial to understand the distinction between supply and quantity supplied. Supply refers to the entire relationship between price and quantity, represented graphically by the supply curve. Quantity supplied, on the other hand, is a specific point on that curve representing the amount supplied at a particular price.
The law of supply is based on the fundamental principle of profit maximization. Producers are motivated to supply more of a good or service when they can sell it at a higher price, as this increases their potential profit. Conversely, if the price falls, they may reduce production to avoid losses or minimize them.
Statements Consistent with the Law of Supply
Several statements can accurately reflect the law of supply. Let's examine some examples:
1. "As the price of coffee beans rises, coffee farmers increase their production."
This statement perfectly aligns with the law of supply. Higher coffee bean prices incentivize farmers to cultivate more coffee, increasing their overall production. The increased price makes coffee farming more profitable, motivating a larger quantity supplied.
2. "When the price of gasoline decreases, gas stations reduce their orders from refineries."
This is another clear example. Lower gasoline prices mean lower profit margins for gas stations. To avoid losses, they order less gasoline from refineries, demonstrating a decrease in quantity supplied in response to a price decrease.
3. "Following a surge in demand for smartphones, manufacturers ramp up production to meet the higher prices."
This situation illustrates the law of supply's dynamic nature. Increased demand initially pushes prices upward. Higher prices then signal to manufacturers that increased production will be profitable, leading them to ramp up their output.
4. "An increase in the price of wheat leads to an expansion of wheat farming acreage."
This example highlights the long-term implications of the law of supply. Higher wheat prices make expanding wheat farming profitable in the long run. Farmers are incentivized to convert land previously used for other crops into wheat fields, leading to an increase in the overall supply of wheat.
5. "With the decrease in the price of cotton, textile mills reduce the volume of cotton they purchase."
Similar to the gasoline example, reduced cotton prices lessen the profit potential for textile mills. This motivates them to reduce their purchases, demonstrating a decrease in quantity supplied in response to a lower price.
Factors Affecting the Supply Curve: Beyond Price
While price is the primary driver in the law of supply, it's crucial to remember the "ceteris paribus" clause. Several other factors can shift the entire supply curve, influencing the quantity supplied at any given price. These are often referred to as supply shifters.
1. Input Prices:
The cost of resources needed to produce a good or service significantly impacts supply. If input prices – such as labor, raw materials, or energy – increase, the supply curve shifts to the left (a decrease in supply). Producers will supply less at each price point due to higher production costs. Conversely, a decrease in input prices shifts the supply curve to the right (an increase in supply).
2. Technology:
Technological advancements can dramatically impact supply. New technologies can reduce production costs, increase efficiency, or enable the production of higher-quality goods. This leads to a rightward shift of the supply curve, as producers can supply more at each price point.
3. Government Policies:
Government regulations, taxes, and subsidies can influence supply. Taxes increase production costs, shifting the supply curve to the left. Subsidies, on the other hand, reduce production costs, shifting the supply curve to the right. Regulations like environmental standards can also affect supply by increasing production costs.
4. Producer Expectations:
Producers' expectations about future prices can influence their current supply decisions. If producers anticipate future price increases, they may reduce current supply to take advantage of higher prices later. Conversely, if they anticipate price decreases, they may increase current supply to avoid losses.
5. Number of Sellers:
An increase in the number of firms producing a good or service will shift the supply curve to the right (increase in supply), as more producers enter the market, increasing the total quantity supplied at each price. The opposite is true when the number of sellers decreases.
6. Natural Events:
Unforeseeable events like natural disasters (hurricanes, droughts, earthquakes) can significantly disrupt supply. These events can damage infrastructure, destroy resources, or directly impact production, leading to a leftward shift of the supply curve.
Statements Inconsistent with the Law of Supply
It's equally important to identify statements that do not reflect the law of supply. These statements often confuse changes in quantity supplied with changes in supply itself.
Incorrect Statement 1: "A hurricane destroyed many coffee farms, resulting in higher coffee prices."
While this statement describes a real-world event, it doesn't illustrate the law of supply. The hurricane caused a decrease in supply (a leftward shift of the supply curve), leading to higher prices. It's not about a change in quantity supplied at a given price.
Incorrect Statement 2: "Increased government regulations on the textile industry caused a decrease in the production of cotton clothes."
Again, this statement describes a shift in the supply curve rather than a movement along it. The government regulations increased production costs, decreasing the supply of cotton clothes (leftward shift).
Real-world Applications and Implications
Understanding the law of supply is crucial for businesses to make informed decisions about production levels, pricing strategies, and resource allocation. It also helps consumers understand why prices fluctuate and how market forces influence the availability of goods and services. For example:
- Businesses: Businesses use the law of supply to determine optimal production levels to maximize profits. By carefully analyzing market demand and price trends, they can adjust their output accordingly.
- Government: Governments utilize this understanding in crafting economic policies. Taxes, subsidies, and regulations all have an impact on supply and can be used to achieve specific economic goals (e.g., stimulating economic growth or protecting the environment).
- Consumers: Consumers can use their knowledge of the law of supply to make informed purchasing decisions. For example, understanding that shortages can cause prices to rise helps them make timely purchases to avoid overpaying.
Conclusion
The law of supply, while seemingly simple, is a powerful tool for understanding how markets function. It highlights the relationship between price and quantity supplied, providing a framework for analyzing market behavior. While price is the primary driver, it's crucial to remember the influence of other factors that can shift the entire supply curve, leading to substantial changes in the quantity supplied even without price changes. By understanding these nuances, individuals and businesses can navigate the complexities of the marketplace with greater clarity and efficiency. Mastering the law of supply is key to making informed decisions in any economic context.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Are The Elements Of A System Of Care
Mar 30, 2025
-
A Challenge That Italy Faced After Unification Was
Mar 30, 2025
-
Why Is Myelin Important Check All That Apply
Mar 30, 2025
-
In Relation To The Wrist The Elbow Is
Mar 30, 2025
-
Correctly Label The Following Parts Of The Digestive System
Mar 30, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Statement Is Consistent With The Law Of Supply . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
