Why Is Myelin Important Check All That Apply.
Breaking News Today
Mar 30, 2025 · 7 min read
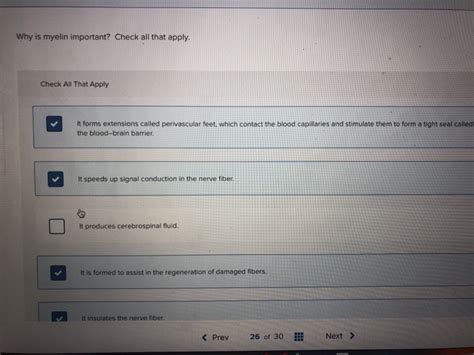
Table of Contents
Why is Myelin Important? Check All That Apply
Myelin, a fatty substance that wraps around nerve fibers (axons), plays a crucial role in the efficient functioning of the nervous system. Its importance extends far beyond simple nerve signal transmission; it's fundamental to cognitive abilities, motor control, and overall neurological health. Understanding why myelin is so important requires examining its multifaceted influence on the brain and body. This article will delve into the various reasons why myelin is essential, covering its impact on nerve conduction speed, signal fidelity, energy efficiency, and the overall health and development of the nervous system.
The Crucial Role of Myelin in Nerve Conduction
Myelin acts as an insulator around axons, similar to the plastic coating on an electrical wire. This insulation prevents the electrical signal (action potential) from leaking out as it travels down the axon. This is the primary reason why myelin is so crucial: it dramatically increases the speed of nerve impulse transmission. Without myelin, signals would travel much slower, leading to significant delays in information processing and motor control.
Saltatory Conduction: The Myelin-Enabled Speed Boost
The myelin sheath isn't continuous; it's segmented, with gaps called Nodes of Ranvier between the myelin segments. The action potential "jumps" from one Node of Ranvier to the next, a process known as saltatory conduction. This "jumping" mechanism is significantly faster than the continuous propagation of action potentials in unmyelinated axons. This speed increase is critical for rapid responses to stimuli, efficient communication between different parts of the nervous system, and the overall speed and precision of cognitive functions. Consider the difference between reacting instantly to a sudden sound versus experiencing a noticeable delay—that delay represents the impact of impaired myelin function.
Myelin's Impact on Signal Fidelity and Precision
Beyond speed, myelin is also crucial for maintaining the fidelity of the nerve signal. Without myelin, the signal would weaken as it travels down the axon, leading to a loss of information and potential errors in communication between neurons. Myelin's insulating properties ensure that the signal arrives at its destination strong and intact, preserving the integrity of the information being transmitted. This accuracy is essential for intricate tasks requiring precise motor control and complex cognitive processing. Consider the fine motor skills involved in playing a musical instrument or performing surgery – these demand precise nerve signaling only achievable with properly functioning myelin.
Preventing Signal Crosstalk: Maintaining Order in the Nervous System
The myelin sheath also helps prevent crosstalk between adjacent axons. In a densely packed nervous system, where numerous axons run close together, myelin acts as a barrier, preventing the signals from one axon from interfering with the signals in neighboring axons. This is vital for ensuring the orderly transmission of information and avoiding confusion in neural pathways. Imagine the chaos if telephone lines were not insulated – a similar scenario occurs in the nervous system without proper myelin insulation.
Energy Efficiency: Myelin's Contribution to Metabolic Optimization
The efficient transmission of nerve signals facilitated by myelin also translates to significant energy savings for the nervous system. Saltatory conduction requires less energy than continuous propagation of action potentials in unmyelinated axons. This energy efficiency is crucial for the brain, which consumes a substantial portion of the body's energy despite its relatively small size. By optimizing energy use, myelin contributes to the overall metabolic health and efficiency of the brain and nervous system. This efficiency is especially important during periods of high cognitive demand or physical activity.
Myelin's Role in Neural Development and Plasticity
Myelin is not merely a static structure; it plays a dynamic role in the development and plasticity of the nervous system. Myelination, the process of forming the myelin sheath, continues throughout childhood and adolescence, contributing significantly to the maturation of cognitive functions and motor skills. This developmental process is essential for achieving optimal brain function and is closely linked to milestones like language acquisition, motor coordination, and higher-order cognitive abilities. Disruptions to myelination during development can have profound and long-lasting effects on neurological function.
Myelin and Neuroplasticity: Adapting to Change
Furthermore, myelin is involved in neuroplasticity, the brain's ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life. This dynamic process is crucial for learning, memory, and recovery from injury. Myelin plays a role in strengthening existing connections and potentially facilitating the formation of new ones. Studies suggest that myelin can be remodeled and adapted in response to experience, reflecting the brain's remarkable capacity for change and adaptation. This plasticity is particularly important in recovering from neurological damage, where the brain may attempt to reroute signals around damaged areas through the creation of new pathways and myelin formation.
The Consequences of Myelin Dysfunction: Neurological Disorders
The importance of myelin is highlighted by the severe consequences of myelin damage or dysfunction. Many neurological disorders, including multiple sclerosis (MS), Guillain-Barré syndrome, and leukodystrophies, are characterized by myelin damage or impaired myelination. These conditions lead to a range of debilitating symptoms, including:
- Slowed nerve conduction: Resulting in weakness, numbness, impaired coordination, and slowed reflexes.
- Sensory disturbances: Affecting vision, hearing, touch, and proprioception (sense of body position).
- Cognitive impairments: Including problems with memory, attention, processing speed, and executive function.
- Motor difficulties: Such as weakness, spasticity, tremors, and gait problems.
These symptoms underscore the fundamental role of myelin in maintaining normal neurological function. The severity of symptoms varies depending on the extent and location of myelin damage. Research continues to investigate the underlying mechanisms of these disorders and explore potential therapies to repair or protect myelin.
Myelin and Age-Related Cognitive Decline
Myelin degradation is also implicated in age-related cognitive decline and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease. As we age, the myelin sheath can become thinner and less efficient, leading to slower nerve conduction and impaired cognitive function. This age-related myelin loss contributes to difficulties with memory, processing speed, and executive function, highlighting the importance of maintaining myelin health throughout life. Research continues to explore strategies to preserve myelin integrity and potentially mitigate age-related cognitive decline.
Lifestyle Factors Influencing Myelin Health
While genetic factors play a role in myelin health, lifestyle choices also have a significant influence. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can contribute to the preservation and optimal functioning of myelin. Key factors include:
- Diet: A diet rich in healthy fats, antioxidants, and vitamins is essential for supporting myelin production and maintenance. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, particularly found in oily fish, are particularly important.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity improves blood flow to the brain, promoting myelin health and supporting neuroplasticity.
- Stress management: Chronic stress can negatively impact myelin health. Practicing stress reduction techniques like yoga, meditation, or mindfulness can help maintain myelin integrity.
- Sleep: Adequate sleep is crucial for brain repair and restoration, including myelin maintenance.
- Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption and smoking: These habits can have detrimental effects on overall health, including myelin health.
Conclusion: The Indispensable Role of Myelin
In conclusion, myelin's importance extends far beyond simply speeding up nerve signals. It is crucial for maintaining signal fidelity, optimizing energy efficiency, facilitating neural development and plasticity, and supporting overall neurological health. The consequences of myelin dysfunction highlight its fundamental role in the nervous system. Maintaining myelin health through lifestyle choices and ongoing research into myelin repair and regeneration are critical for preserving cognitive function, motor skills, and overall well-being throughout life. The multifaceted nature of myelin's influence underscores its indispensable role in ensuring the optimal functioning of the human nervous system. Further research continues to unravel the complexities of myelin's function and its implications for various neurological conditions and age-related cognitive decline. Understanding its vital role emphasizes the importance of prioritizing lifestyle factors and seeking medical attention when myelin-related issues are suspected.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Total Of Amalas Liabilities
Apr 01, 2025
-
A Patient Who Has Experienced A Back Injury
Apr 01, 2025
-
Define Back Channel Cues List 3 Examples Of Backchannel Cues
Apr 01, 2025
-
How Does Madison Use Comparison To Bolster His Argument
Apr 01, 2025
-
Afferent Signals From External Stimuli Are Carried By The
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Why Is Myelin Important Check All That Apply. . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
