Which Statement Summarizes The Process Of Ovulation
Breaking News Today
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
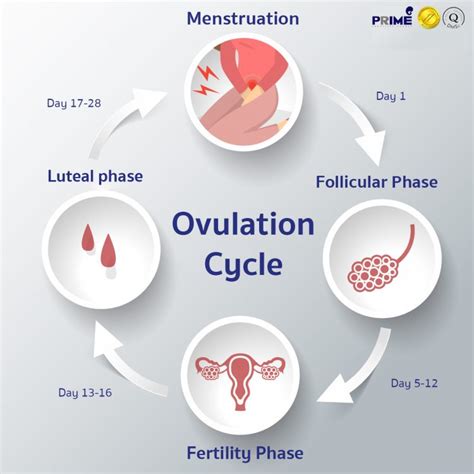
Table of Contents
Which Statement Summarizes the Process of Ovulation? A Comprehensive Guide
Ovulation, a pivotal event in the female reproductive cycle, is a complex process involving the maturation and release of an egg from the ovary. Understanding this process is crucial for anyone seeking to understand fertility, contraception, and women's health in general. While many statements attempt to summarize ovulation, a truly comprehensive explanation requires delving into the intricate hormonal and physiological mechanisms involved. This article will explore these mechanisms in detail, ultimately providing a nuanced summary that encapsulates the entire process.
The Hormonal Orchestra: Orchestrating Ovulation
The process of ovulation isn't a singular event but rather the culmination of a carefully orchestrated sequence of hormonal events throughout the menstrual cycle. These hormones, primarily secreted by the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and ovaries, act in a feedback loop, ensuring the timely maturation and release of a mature ovum.
1. The Hypothalamus: The Conductor
The hypothalamus, a small region in the brain, initiates the process by releasing gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). This hormone acts as the conductor of the endocrine orchestra, stimulating the anterior pituitary gland.
2. The Pituitary Gland: The Instrumentalists
The anterior pituitary gland, in response to GnRH, secretes two crucial gonadotropins:
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH): FSH primarily targets the ovaries, stimulating the growth and maturation of several ovarian follicles. Each follicle contains an immature egg (oocyte).
- Luteinizing hormone (LH): LH plays a more crucial role in the final stages of ovulation. While it also contributes to follicle development, its primary function is triggering the final maturation and release of the egg.
3. The Ovaries: The Soloists
The ovaries respond to FSH and LH by producing estrogen, a steroid hormone vital for follicle development and maturation. As follicles grow, they produce increasing amounts of estrogen. This rising estrogen level provides crucial feedback to the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
4. The Positive Feedback Loop: The Crescendo
The rising estrogen levels initially exert a negative feedback effect, suppressing GnRH and LH secretion. However, as estrogen levels reach a critical threshold, they trigger a positive feedback loop. This positive feedback loop leads to a dramatic surge in LH secretion, the hallmark of the pre-ovulatory phase.
The Ovulatory Event: The Grand Finale
The LH surge, the pivotal moment, triggers the final maturation of the dominant follicle and initiates the process of ovulation. This surge causes:
- Final Oocyte Maturation: The oocyte completes its meiotic division, becoming a mature ovum ready for fertilization.
- Follicle Rupture: The mature follicle swells and weakens, ultimately rupturing, releasing the mature ovum into the fallopian tube.
- Corpus Luteum Formation: After the ovum is released, the ruptured follicle transforms into the corpus luteum, a temporary endocrine gland. The corpus luteum produces progesterone, essential for preparing the uterine lining for potential implantation of a fertilized egg.
Post-Ovulation: The Encore
Following ovulation, the corpus luteum continues to produce progesterone and estrogen. If fertilization occurs, the corpus luteum persists, producing hormones vital for maintaining pregnancy. If fertilization doesn't occur, the corpus luteum eventually degenerates, leading to a decline in progesterone and estrogen levels, initiating menstruation.
Summarizing the Process: A Concise Overview
Ovulation is the process where a mature egg is released from the ovary, driven by a complex interplay of hormones within the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis. This process begins with the hypothalamus releasing GnRH, stimulating the pituitary gland to release FSH and LH. FSH initiates follicle development, while the increasing estrogen produced by these follicles ultimately triggers a surge in LH. This LH surge is the critical trigger for final oocyte maturation, follicle rupture, and the release of the mature ovum into the fallopian tube. The ruptured follicle transforms into the corpus luteum, producing progesterone crucial for preparing the uterus for potential implantation.
Factors Influencing Ovulation: The Stage Crew
Several factors can influence the regularity and timing of ovulation:
- Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance, leading to irregular or absent ovulation.
- Weight: Both underweight and overweight can interfere with ovulation due to hormonal imbalances.
- Exercise: Excessive exercise can suppress ovulation, while moderate exercise is generally beneficial.
- Age: Ovulation becomes less regular and eventually ceases with age, marking the transition to menopause.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can significantly affect ovulation.
- Medications: Some medications, including certain antidepressants and antipsychotics, can interfere with ovulation.
Understanding Ovulation: Its Significance
Understanding ovulation is crucial for various aspects of women's health:
- Family Planning: Tracking ovulation is essential for couples trying to conceive or using natural family planning methods for contraception.
- Fertility Treatments: In vitro fertilization (IVF) and other assisted reproductive technologies rely heavily on a precise understanding of ovulation timing.
- Diagnosing Fertility Issues: Irregular or absent ovulation is a common cause of infertility, and its diagnosis is vital for appropriate treatment.
- Managing Menstrual Disorders: Understanding ovulation is crucial for managing conditions like amenorrhea (absence of menstruation) and dysmenorrhea (painful menstruation).
Detecting Ovulation: The Spotlights
Several methods can help women detect ovulation:
- Basal Body Temperature (BBT): BBT charting involves tracking body temperature daily, noting a slight increase after ovulation.
- Cervical Mucus: Changes in cervical mucus consistency and quantity can indicate ovulation.
- Ovulation Predictor Kits (OPKs): OPKs detect the LH surge in urine, providing a relatively accurate prediction of ovulation.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasound scans can directly visualize follicle development and ovulation.
Conclusion: The Curtain Call
Ovulation, a multifaceted process, is a critical event in the female reproductive cycle. It is the culmination of a complex interplay of hormonal events, culminating in the release of a mature ovum ready for fertilization. Understanding this intricate process is vital for individuals seeking to manage their reproductive health, plan families, or address fertility concerns. By understanding the hormonal orchestration, the ovulatory event itself, and the factors influencing this process, individuals can gain a comprehensive appreciation of this fundamental aspect of female biology. This knowledge empowers women to make informed decisions about their reproductive health and family planning.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
You Are At A Local Restaurant With Colleagues
Mar 22, 2025
-
The Law Of Increasing Opportunity Costs States That
Mar 22, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Occurs During Inhalation
Mar 22, 2025
-
A Patient With Bilateral Pain Hurts On
Mar 22, 2025
-
Sodium 24 Has A Half Life Of 15 Hours
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Statement Summarizes The Process Of Ovulation . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
