Words In Spanish That End With Ar
Breaking News Today
Mar 28, 2025 · 6 min read
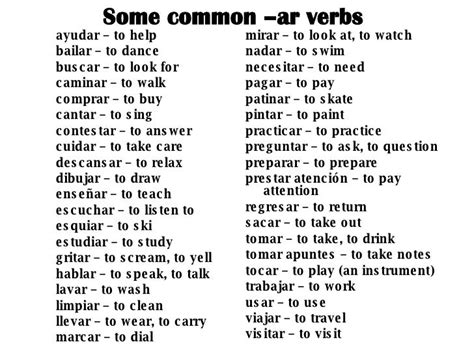
Table of Contents
Spanish Words Ending in "-ar": A Comprehensive Guide
Spanish is a beautiful and vibrant language, rich in vocabulary and expressive nuances. One fascinating aspect of Spanish morphology is the prevalence of verbs ending in "-ar," the most common verb conjugation pattern. But the "-ar" suffix isn't limited to verbs; it also appears in a surprisingly diverse range of nouns, adjectives, and adverbs. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the world of Spanish words ending in "-ar," exploring their various forms, origins, and usage within the context of the language.
Understanding the "-ar" Suffix
The "-ar" suffix in Spanish is primarily associated with infinitive verbs. These are the base form of verbs, indicating the action without specifying tense or subject. Examples include:
- Hablar: To speak
- Caminar: To walk
- Trabajar: To work
- Amar: To love
- Cantar: To sing
However, the "-ar" suffix isn't solely confined to verbs. Let's explore its presence in other word classes.
Nouns Ending in "-ar"
While less common than verb infinitives, several nouns in Spanish end in "-ar." These often derive from verbs or have a connection to actions or characteristics.
Examples of Nouns Ending in "-ar":
- Azúcar: Sugar (from Arabic) - Though seemingly unrelated to verbs at first glance, the word's history reveals a link to earlier forms, illustrating the evolution of the Spanish language.
- Radar: Radar (from English) - This is a borrowed word, showing the dynamic nature of language and its borrowing from other sources. Note that the suffix remains consistent in the adapted form.
- Pulpar: Pulp (often referring to fruit pulp) - A prime example of a noun directly related to its verb form, "pulpar," meaning "to make into pulp".
- Cenar: Dinner - This word's root is in the verb "cenar," meaning "to have dinner," showcasing the close relationship between verbs and their associated nouns.
- Alisar: To smooth, to flatten (also used as a noun to refer to the action of smoothing) - This example shows the dual nature of some words, functioning as both verb and noun depending on context.
The presence of nouns ending in "-ar" highlights the flexibility of the Spanish language and the fluidity between verb actions and their resulting nouns.
Adjectives Ending in "-ar"
Adjectives are descriptive words that modify nouns. While less frequent than nouns or verbs ending in "-ar," some adjectives in Spanish also feature this suffix. Often, these adjectives are derived from verbs or have a related semantic connection.
Examples of Adjectives Ending in "-ar":
- Popular: Popular – This adjective describes something widely liked or favored, hinting at a possible connection to the idea of "people" (pueblo).
- Modular: Modular – This adjective describes something composed of standardized units or modules, suggesting a connection to the act of structuring or arranging. The word likely shows the influence of Latin.
- Regular: Regular – This adjective describes something that is consistent or patterned, suggesting a connection to rules or established norms. This word, with its Latin roots, shows a clear link to the word "rule".
While rarer than nouns or verbs, the existence of adjectives ending in "-ar" emphasizes the multifaceted usage of this suffix within Spanish word formations.
Adverbs Ending in "-ar"
Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, providing additional information about the action, state, or quality being described. The use of "-ar" in adverbs is quite uncommon. It's more likely that a word that looks like an adverb in "-ar" is actually the infinitive form of a verb acting as a command.
Examples of Words that Seem to be Adverbs in "-ar":
- Hablar: (infinitive) Speak! In the imperative mood, this functions as a command.
- Caminar: (infinitive) Walk! Another example of an infinitive functioning as a command in the imperative mood.
The apparent rarity of adverbs ending in "-ar" is a reflection of the less frequent use of this suffix in modifying descriptive elements within sentences.
Regional Variations and Dialects
The use and prevalence of words ending in "-ar" can vary slightly across different Spanish-speaking regions. Certain words might be more common in one country or region than in another, reflecting the rich diversity within the language. While the core grammatical rules remain consistent, subtle differences in vocabulary and usage can be observed.
The Etymology of "-ar"
Understanding the etymology of the "-ar" suffix sheds light on its widespread usage in Spanish. It is largely derived from Latin verb conjugations, inheriting its significance from the Romance language family. The "-are" ending in Latin evolved into "-ar" in Spanish, maintaining its core function of indicating verbs. This historical link underscores the deep-rooted connection between Latin and the modern Spanish language.
The Importance of Context
The meaning and function of words ending in "-ar" heavily rely on context. A word like "hablar," for example, can be interpreted as "to speak," "speaking," or even "speak!" (an imperative command) depending on its placement within a sentence. Recognizing the grammatical role and surrounding words is crucial for accurate interpretation.
Practical Applications and Exercises
To solidify your understanding of words ending in "-ar," consider these exercises:
-
Verb Conjugation: Practice conjugating various "-ar" verbs in different tenses (present, past, future, etc.). This will enhance your grasp of verb morphology.
-
Sentence Construction: Create sentences using different nouns, adjectives (if applicable), and verbs ending in "-ar." Experiment with different sentence structures to further strengthen your understanding.
-
Word Recognition: Engage in reading exercises focusing on identifying and understanding words ending in "-ar" within larger texts. This will enhance your vocabulary and contextual comprehension.
-
Translation: Practice translating sentences containing words ending in "-ar" between Spanish and your native language. This will reinforce your understanding of their usage in different contexts.
Conclusion
The "-ar" suffix represents a significant element in Spanish grammar and vocabulary. While predominantly associated with verb infinitives, its presence in nouns and adjectives, albeit less frequent, showcases the adaptability and richness of the Spanish language. By understanding its etymology, variations in usage, and contextual significance, you can significantly enhance your comprehension and fluency in Spanish. This deep dive into "-ar" words offers a clearer picture of the intricate structure and evolution of the Spanish language, proving it to be more than just the sum of its parts. Through further exploration and practice, you can unlock a deeper appreciation for the beauty and complexity of this widely spoken language. The journey of mastering Spanish continues with every new word learned, and the "-ar" suffix serves as a testament to the continuous evolution and dynamic nature of language itself. Remember to practice regularly, and you will soon find yourself comfortable and confident in your ability to understand and use words ending in "-ar" fluently.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Anatomy And Physiology 2 Exam 1 Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
Fluid Electrolyte And Acid Base Balance Ati Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
Functionalist Psychologists Focus On The Function Of Behavior And
Mar 31, 2025
-
Functions Of The Large Intestine Include Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
-
An Interval Of An Ecg Is Quizlet
Mar 31, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Words In Spanish That End With Ar . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
