What Is Also Called A Substitution Process
Breaking News Today
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
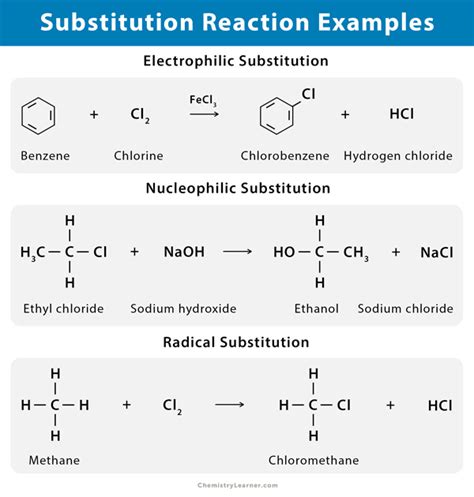
Table of Contents
What is Also Called a Substitution Process? A Deep Dive into Diverse Applications
The term "substitution process" isn't a rigidly defined term across all fields. Instead, it's a descriptive phrase used to refer to a wide range of processes where one element, component, or value is replaced with another. This replacement can occur in various contexts, from chemical reactions and cryptography to data processing and even linguistic analysis. To truly understand what's meant by a "substitution process," we need to explore its diverse manifestations in different domains.
Substitution in Chemistry: Reactions and Transformations
In chemistry, substitution reactions are a cornerstone of organic chemistry. These reactions involve the replacement of one atom or group of atoms (a substituent) in a molecule with another atom or group. This often involves breaking a chemical bond and forming a new one.
Types of Chemical Substitution Reactions:
-
Nucleophilic Substitution: This type of reaction involves a nucleophile (an electron-rich species) attacking an electrophile (an electron-deficient species), leading to the substitution of a leaving group. Examples include SN1 and SN2 reactions, which differ in their mechanisms and stereochemistry. Understanding the difference between SN1 and SN2 is crucial for predicting reaction outcomes and designing synthetic pathways.
-
Electrophilic Substitution: In this case, an electrophile attacks an electron-rich molecule, substituting a hydrogen atom or another group. This is particularly common in aromatic compounds like benzene, where the electrophile replaces a hydrogen atom on the aromatic ring. Examples include nitration, halogenation, and Friedel-Crafts alkylation/acylation. These reactions are vital for synthesizing a wide array of aromatic compounds with specific functionalities.
-
Radical Substitution: These reactions involve free radicals—atoms or molecules with unpaired electrons—as intermediates. A free radical attacks a molecule, abstracting an atom (usually hydrogen) and forming a new radical. This process can continue in a chain reaction. Halogenation of alkanes is a classic example of a radical substitution reaction. Understanding the reaction mechanism and controlling the reaction conditions are key to achieving desired products.
The importance of understanding substitution reactions in chemistry cannot be overstated. They form the basis of numerous industrial processes, allowing the synthesis of a vast array of chemicals used in everyday life, from pharmaceuticals and plastics to fuels and solvents. Furthermore, mastering substitution reactions is essential for researchers in fields like medicinal chemistry, materials science, and polymer chemistry.
Substitution in Cryptography: Ciphers and Codebreaking
In cryptography, substitution is a fundamental technique used in ciphers. Substitution ciphers replace individual letters or groups of letters with different letters or symbols.
Types of Substitution Ciphers:
-
Caesar Cipher: This is one of the simplest substitution ciphers. Each letter in the plaintext is replaced by a letter a fixed number of positions down the alphabet. For example, a Caesar cipher with a shift of 3 would replace 'A' with 'D', 'B' with 'E', and so on. While simple, it demonstrates the basic principle of substitution.
-
Monoalphabetic Substitution: Each letter in the alphabet is consistently mapped to a different letter or symbol. The key is the specific mapping used. Though more secure than the Caesar cipher, monoalphabetic substitution is vulnerable to frequency analysis.
-
Polyalphabetic Substitution: This improves on monoalphabetic substitution by using multiple substitution alphabets. The specific alphabet used depends on the position of the letter in the plaintext. The Vigenère cipher is a classic example of a polyalphabetic substitution cipher, offering significantly improved security compared to monoalphabetic methods.
Substitution ciphers have a rich history, playing a crucial role in protecting sensitive information throughout history. While many modern ciphers are far more complex, understanding substitution techniques provides a foundation for appreciating the evolution of cryptography and the ongoing battle between codemakers and codebreakers. The development of more sophisticated ciphers, including those based on public-key cryptography, has rendered simple substitution ciphers insecure for most applications, but their historical significance and underlying principles remain relevant to the study of cryptography.
Substitution in Data Processing: Algorithms and Transformations
In data processing and computer science, substitution refers to various algorithms and techniques that replace one data element with another. This can involve replacing values, characters, or even entire data structures.
Applications of Substitution in Data Processing:
-
Data Cleaning: Substitution is often used to handle missing values in datasets. Missing data can be replaced with the mean, median, mode, or other imputed values. This process aims to improve data quality and enable more effective analysis.
-
Data Transformation: Substitution can be part of broader data transformation techniques, such as normalization or standardization. Values might be replaced with their z-scores or scaled to a specific range. This is crucial for various data analysis techniques, particularly those sensitive to the scale and distribution of data.
-
String Manipulation: In string processing, substitution involves replacing specific substrings within a string with other substrings. This is a common task in text processing, natural language processing, and software development. Regular expressions are a powerful tool for performing complex string substitutions.
-
Search and Replace Operations: Many text editors and word processors offer search and replace functionality, which is a direct application of substitution. The user specifies a pattern to search for and a replacement string, allowing for efficient modification of text documents. This is an extremely common and widely used application of the substitution process.
Substitution in Linguistic Analysis: Morphology and Semantics
In linguistics, substitution refers to replacing one word or phrase with another while maintaining the overall grammatical structure and meaning (or at least a related meaning).
Applications of Substitution in Linguistics:
-
Synonym Replacement: Substituting a word with its synonym can add variety and improve readability. This is a crucial technique in writing and editing.
-
Paraphrasing: Replacing phrases or clauses with equivalent expressions creates paraphrases. Paraphrasing is useful for clarifying meaning, avoiding repetition, and improving the flow of text.
-
Anaphora Resolution: This involves replacing pronouns or other anaphoric expressions with their referents. Understanding anaphora is vital in natural language processing. Correctly resolving anaphora is critical for accurately interpreting text and extracting meaning.
-
Morphological Analysis: In morphology, substitution can be used to identify morphemes (the smallest units of meaning) within words. By substituting parts of words and observing changes in meaning, linguists can uncover the underlying structure of words and their components.
Substitution in Other Contexts: A Broader Perspective
The concept of substitution extends beyond the specific examples mentioned above. It appears in numerous other areas, including:
-
Genetics: Gene substitution, also known as gene replacement, is a technique used in genetic engineering where a gene is replaced with another gene.
-
Finance: Substitution effects in economics refer to changes in consumption patterns due to changes in relative prices.
-
Art and Design: Substitution can refer to replacing one element in a design or artwork with another, altering the overall aesthetic or message.
-
Game Theory: Strategic substitution in game theory involves players replacing one strategy with another in response to the actions of other players.
The pervasiveness of the substitution process highlights its fundamental role in diverse fields. Its applications are constantly evolving with technological advancements and new discoveries. Understanding the underlying principles of substitution is therefore crucial for anyone working in a field involving transformation, manipulation, or replacement of elements.
In conclusion, the term "substitution process" encompasses a broad range of activities, all united by the common thread of replacing one element with another. The specific nature of the substitution and its implications vary widely depending on the context. Whether it's in the precise reactions of chemical compounds, the intricate workings of cryptographic algorithms, the efficient processing of data, or the nuanced interpretations of linguistics, the substitution process reveals its enduring and versatile presence across many disciplines. The detailed exploration of each domain demonstrates not only the versatility of this concept but also the critical role it plays in shaping our understanding of various systems and phenomena.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Class V Issue And Turn In Procedures For Using Units
Mar 21, 2025
-
When The Atria Contract Which Of The Following Is True
Mar 21, 2025
-
Unit 4 Progress Check Mcq Part B
Mar 21, 2025
-
Signs And Symptoms Of A Sympathomimetic Drug Overdose Include
Mar 21, 2025
-
Approximately 75 Percent Of Struck By Fatalities Involve
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Also Called A Substitution Process . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
